Guanosina
| Guanosina | |
|---|---|
 | |
2-Amino-9-[3,4-dihidroxi-5-(hidroximetil)oxolan-2-il]-3H-purin-6-ona | |
Outros nomes Guanina ribósido | |
| Identificadores | |
| Número CAS | 118-00-3 |
| PubChem | 765 |
| ChemSpider | 6544 |
| UNII | 12133JR80S |
| DrugBank | DB02857 |
| KEGG | C00387 |
| MeSH | Guanosine |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:16750 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL375655 |
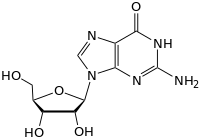
| Imaxes 3D Jmol | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Propiedades | |
| Fórmula molecular | C10H13N5O5 |
| Masa molecular | 283,241 |
Se non se indica outra cousa, os datos están tomados en condicións estándar de 25 °C e 100 kPa. | |
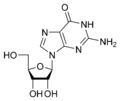
A guanosina é un nucleósido purínico composto pola base nitroxenada guanina unida ao azucre ribosa (ribofuranosa) por enlace β-N9-glicosídico. O seu nome IUPAC é: 2-Amino-9-[3,4-dihidroxi-5-(hidroximetil)oxolan-2-il]-3H-purin-6-ona. Un derivado oxidado seu é a 8-oxoguanosina, que se usa como biomarcador de estrés oxidativo.
Características
[editar | editar a fonte]Cando a guanina está unida á 2-desoxirribosa en lugar de á ribosa, orixínase a desoxiguanosina. Cando a esta se lle une un fosfato en posición 5' orixina o nucleótido dGMP. A 8-oxo-2'-desoxiguanosina é un derivado oxidado da desoxiguanosina, orixinado durante a oxidación do ADN[1].
Se a guanosina é fosforilada convértese no nucleótido guanosín monofosfato (GMP), da que derivan outros como o GMPc, GDP e GTP, que exercen importantes funcións biolóxicas.
A estrutura da guanosina ten grandes semellanzas coas do fármaco antiviral aciclovir[2], usado no tratamento do herpes.
A guanosina requírese como cofactor para o splicing do ARN durante o "auto-splicing" dun intrón do grupo I, como por exemplo os do pre-ARNr do protozoo Tetrahymena, xa que a guanosina ataca o sitio de splicing 5' do intrón.[3]
Degradación da guanosina
[editar | editar a fonte]A guanosina (procedente da degradación do GMP pola 5'-nucleotidase) produce ribosa e guanina pola acción do encima nucleosidase. A ribosa pode volverse a reutilizar. A guanina pode seguir degradándose dando xantina e finalmente ácido úrico, que é excretado polos primates.
-
Estrutura química da guanosina.
-
A 8-oxoguanosina é un derivado oxidado da guanosina.
-
Estrutura química da 2-desoxiguanosina.
-
A 8-oxo-2'-desoxiadenosina é un derivado oxidado da desoxiadenosina.
-
Comparación das estruturas da guanosina e do aciclovir.
Notas
[editar | editar a fonte]- ↑ Nadja C. de Souza-Pinto, Lars Eide, Barbara A. Hogue, Tanja Thybo, Tinna Stevnsner, Erling Seeberg, Arne Klungland, and Vilhelm A. Bohr (2001). "Repair of 8-Oxodeoxyguanosine Lesions in Mitochondrial DNA Depends on the Oxoguanine DNA Glycosylase (OGG1) Gene and 8-Oxoguanine Accumulates in the Mitochondrial DNA of OGG1-defective Mice". Cancer Research 61 (14): 5378–5381. PMID 11454679.
- ↑ [1] Características do aciclovir.
- ↑ [2] US National Library of Medicine - National Institutes of Health.
Véxase tamén
[editar | editar a fonte]Outros artigos
[editar | editar a fonte]Tipos de ácidos nucleicos | |
|---|---|
| Bases nitroxenadas | Púricas (Purina): Adenina · Guanina · Hipoxantina · Xantina · Pirimidínicas (Pirimidina): Citosina · Timina · Uracilo |
| Nucleósidos | Adenosina · Uridina · Guanosina · Citidina · Desoxiadenosina · Timidina · Desoxiguanosina · Desoxicitidina · Inosina |
| Nucleótidos (nucleósidos monofosfato) | |
| Nucleósidos difosfato | |
| Nucleósidos trifosfato | |
| Desoxinucleótidos e desoxirribonucleósidos difosfato e trifosfato | |
| Ácidos ribonucleicos | |
| Ácidos desoxirribonucleicos | |
| Análogos de ácidos nucleicos | |
| Secuencias | |
Principais familias bioquímicas Alcaloides · Aminoácidos · Carbohidratos · Carotenoides · Cofactores enzimáticos · Esteroides · Flavonoides · Glicósidos · Lípidos · Péptidos · Policétidos · Tatrapirrois · Terpenos | |
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.