福特-富尔克森算法
福特-富尔克森方法(英語:Ford–Fulkerson method),又稱福特-富尔克森算法(Ford–Fulkerson algorithm),是一类计算网络流的最大流的贪心算法。之所以称之为“方法”而不是“算法”,是因为它寻找增广路径的方式并不是完全确定的,而是有几种不同时间复杂度的实现方式[1][2]。它在1956年由小萊斯特·倫道夫·福特及德爾伯特·雷·富爾克森[3]发表。“福特-富尔克森”这个名词通常也指代埃德蒙兹-卡普算法,这是一个特殊的福特-富尔克森算法实现。
算法的思想如下:只要有一条从源点(开始节点)到汇点(结束节点)的路径,在路径的所有边上都有可用容量,就沿着这条路径发送一个流,流量由路径上的最小容量限制。 然后再找到另一条路径,一直到网络中不存在这种路径为止。 一条有可用容量的路径被称为一条增广路径。
算法
[编辑]设为一个图,并且为每条从到的边设置一个最大流量,并且初始化当前流量。下面是该算法每一步的实现:
容量限制: 每条边上的流都不能超出边的最大流量。 反向对称: 从到的流量一定是从到的流量的相反数(见样例)。 流量守恒: 除非是源点或汇点,一个节点的净流量为零。 f的值: 从源点流出的流量一定等于汇点接收的流量。
这意味着每轮计算之后通过网络的都是一个流。我们定义残留网络 是一个网络的剩余流量。注意残留网络可以设置从到的流量,即使在原先的网络中不允许这种情况产生:如果 但 ,那么:也即,从到的流量给从到的流量提供了额外的剩余量。
伪代码
[编辑]算法 福特-富尔克森
- 输入 给定一张边的容量为的图,源点以及汇点。
- 输出 在网络中,从到的最大流。
- 初始化网络流量、残留网络。对于图的每一条边,初始化流量。
- 只要中还存在一条从到的路径,使对于每一条边,都有:
- 设置路径本次应发送的流量为路径最小剩余流量:。
- 更新网络流量。
- 对于每一条边,更新的剩余流量:
- (在路径中“发送”流)
- (这个流在之后可以被“发送”回来)
步骤2中的路径可以用广度优先搜索或深度优先搜索在中找到。如果使用了广度优先搜索,这个算法就是Edmonds–Karp算法。
当步骤2中找不到可行路径时,就无法在残留网络中到达。设是在残留网络中可以到达的节点的集合,然后从到的其余部分的网络一方面等于我们找到的从到的所有流的总流量,另一方面所有这样的流量组成了一个上限。这说明我们找到的流是最大的。参见最大流最小割定理。
如果图有多个源点和汇点,可以按如下方法处理:设,。 添加一个新源点与所有源点有一条边相连,容量。添加一个新汇点与所有汇点 有一条边相连,容量。然后执行福特-富尔克森算法。
同样的,如果节点有通过限制,可将这个节点用两个节点替换,用一条边相连,容量为。然后执行福特-富尔克森算法。
复杂度
[编辑]算法通过添加找到的增广路径的流量增加总流量,当无法找到增广路径时,总流量就达到了最大。当流量是整数时,福特-富尔克森算法的运行时间为(参见大O符号), 图中的边数,为最大流。 这是因为一条增广路径可以在的时间复杂度内找到,每轮算法执行后流量的增长至少为。但是在极端情况下,算法有可能永远不会停止。
福特-富尔克森算法的一个特例是埃德蒙兹-卡普算法,时间复杂度为。
样例
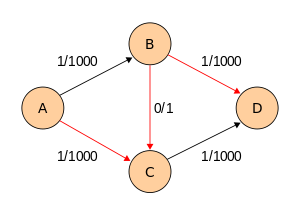
[编辑]下面的样例演示了福特-富尔克森在一张有4个节点,源点为,汇点为的图中的第一轮计算。 这个例子显示了算法在最坏情况下的行为。在每一轮算法中,只有的流量被发送至网络中。如果算法改用宽度优先搜索,那么只需要两轮计算。
| 路径 | 容量 | 网络 |
|---|---|---|
| 原流 | 
| |

| ||
| ||
| 1998轮之后… | ||
| 最终流 | 
| |
注意当找到路径时,流是如何从发送至的。
无法终止算法的样例
[编辑]
右图所示的网络中源点为,汇点为边、、的容量为, 和,使。其它所有边的容量。 使用福特-富尔克森算法可找到三条增广路径,分别为、、.
| 步骤 | 增广路径 | 发送流 | 剩余容量 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | |||||
| 1 | |||||
| 2 | |||||
| 3 | |||||
| 4 | |||||
| 5 | |||||
注意在步骤1和步骤5之后,边、、的残留容量都可以表示为、或,同时,对于一些特殊的这意味着算法可以通过、、与 无限增广,并且残留容量总处于一个循环。在步骤5之后网络的流为,如果继续用以上的算法增广,总的流将向趋近,但最大流为。在这个样例中,算法将永远不会停止,且结果也不会向实际的最大流趋近。[4]
Python源码
[编辑]class Edge(object):
def __init__(self, u, v, w):
self.source = u
self.sink = v
self.capacity = w
def __repr__(self):
return "%s->%s:%s" % (self.source, self.sink, self.capacity)
class FlowNetwork(object):
def __init__(self):
self.adj = {}
self.flow = {}
def add_vertex(self, vertex):
self.adj[vertex] = []
def get_edges(self, v):
return self.adj[v]
def add_edge(self, u, v, w=0):
if u == v:
raise ValueError("u == v")
edge = Edge(u,v,w)
redge = Edge(v,u,0)
edge.redge = redge
redge.redge = edge
self.adj[u].append(edge)
self.adj[v].append(redge)
self.flow[edge] = 0
self.flow[redge] = 0
def find_path(self, source, sink, path):
if source == sink:
return path
for edge in self.get_edges(source):
residual = edge.capacity - self.flow[edge]
if residual > 0 and edge not in path:
result = self.find_path( edge.sink, sink, path + [edge])
if result != None:
return result
def max_flow(self, source, sink):
path = self.find_path(source, sink, [])
while path != None:
residuals = [edge.capacity - self.flow[edge] for edge in path]
flow = min(residuals)
for edge in path:
self.flow[edge] += flow
self.flow[edge.redge] -= flow
path = self.find_path(source, sink, [])
return sum(self.flow[edge] for edge in self.get_edges(source))
使用样例
[编辑]>>> g = FlowNetwork()
>>> [g.add_vertex(v) for v in "sopqrt"]
[None, None, None, None, None, None]
>>>
>>> g.add_edge('s','o',3)
>>> g.add_edge('s','p',3)
>>> g.add_edge('o','p',2)
>>> g.add_edge('o','q',3)
>>> g.add_edge('p','r',2)
>>> g.add_edge('r','t',3)
>>> g.add_edge('q','r',4)
>>> g.add_edge('q','t',2)
>>> print (g.max_flow('s','t'))
5
应用
[编辑]二分图的最大匹配
最大不相交路径
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ Laung-Terng Wang, Yao-Wen Chang, Kwang-Ting (Tim) Cheng. Electronic Design Automation: Synthesis, Verification, and Test. Morgan Kaufmann. 2009: 204. ISBN 0080922007.
- ^ Thomas H. Cormen; Charles E. Leiserson; Ronald L. Rivest; Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms. MIT Press. 2009: 714. ISBN 0262258102.
- ^ Ford, L. R.; Fulkerson, D. R. Maximal flow through a network. Canadian Journal of Mathematics. 1956, 8: 399. doi:10.4153/CJM-1956-045-5.
- ^ Zwick, Uri. The smallest networks on which the Ford–Fulkerson maximum flow procedure may fail to terminate. Theoretical Computer Science. 21 August 1995, 148 (1): 165–170. doi:10.1016/0304-3975(95)00022-O.
- Cormen, Thomas H.; Leiserson, Charles E.; Rivest, Ronald L.; Stein, Clifford. Section 26.2: The Ford–Fulkerson method. Introduction to Algorithms Second. MIT Press and McGraw–Hill. 2001: 651–664. ISBN 0-262-03293-7.
- George T. Heineman; Gary Pollice; Stanley Selkow. Chapter 8:Network Flow Algorithms. Algorithms in a Nutshell. Oreilly Media. 2008: 226–250. ISBN 978-0-596-51624-6.
- Jon Kleinberg; Éva Tardos. Chapter 7:Extensions to the Maximum-Flow Problem. Algorithm Design. Pearson Education. 2006: 378–384. ISBN 0-321-29535-8.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.





















































































