选择排序
| 选择排序 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 概况 | |
| 類別 | 排序算法 |
| 資料結構 | 數組 |
| 复杂度 | |
| 平均時間複雜度 | |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | |
| 最优时间复杂度 | |
| 空間複雜度 | 總共,需要輔助空間 |
| 最佳解 | 偶尔出现 |
| 相关变量的定义 | |
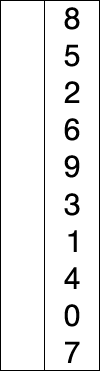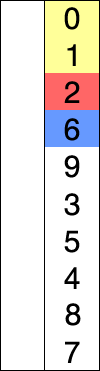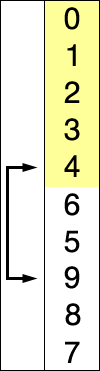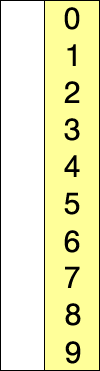
选择排序(英語:Selection sort)是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理如下。首先在未排序序列中找到最小(大)元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,然后,再从剩余未排序元素中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾。以此类推,直到所有元素均排序完毕。
选择排序的主要优点与数据移动有关。如果某个元素位于正确的最终位置上,则它不会被移动。选择排序每次交换一对元素,它们当中至少有一个将被移到其最终位置上,因此对个元素的表进行排序总共进行至多次交换。在所有的完全依靠交换去移动元素的排序方法中,选择排序属于非常好的一种。
實作範例
C语言
void selection_sort(int a[], int len)
{
int i,j,temp;
for (i = 0 ; i < len - 1 ; i++)
{
int min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++) //走訪未排序的元素
{
if (a[j] < a[min]) //找到目前最小值
{
min = j; //紀錄最小值
}
}
if(min != i)
{
temp=a[min]; //交換兩個變數
a[min]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
}
/* swap(&a[min], &a[i]); */ //做交換
}
}
/*
void swap(int *a,int *b) //交換兩個變數
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
*/
Java
public class SelectionSort {
public void sort(int[] arr) {
int minIndex;
for(int i = 0;i < arr.length;i++) {
minIndex = i;
//遍历找出未排序中的元素中最小值下标
for(int j = i;j < arr.length;j++) {
if(arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
//若最小值下标与未排序中最左侧下标不一致则交换
if(minIndex != i) {
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[minIndex];
arr[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
}
Julia (程式語言)
# Julia Sample:SelectionSort
function SelectionSort(A)
for i=1:length(A)
min=i
for j=i+1:length(A)
min=A[j]<A[min]?j:nothing # Get Min
if min!=i
A[min],A[i]=A[i],A[min] # Swap
end
end
end
return A
end
# Main Code
A = [16,586,1,31,354,43,3]
println(A) # Original Array
println(SelectionSort(A)) # Selection Sort Array
Python
def selection_sort(list1):
longs = len(list1)
for i in range(longs-1):
idx = i
for j in range(i, longs):
if list1[j] < list1[idx]:
idx = j
if idx != i:
list1[i], list1[idx] = list1[idx], list1[i]
复杂度分析
选择排序的交换操作介于和次之间。选择排序的比较操作为次。选择排序的赋值操作介于和次之间。
比较次数,比较次数与关键字的初始状态无关,总的比较次数。交换次数,最好情况是,已经有序,交换0次;最坏情况是,逆序,交换次。交换次数比冒泡排序较少,由于交换所需CPU时间比比较所需的CPU时间多,值较小时,选择排序比冒泡排序快。
原地操作几乎是选择排序的唯一优点,当空间复杂度要求较高时,可以考虑选择排序;实际适用的场合非常罕见。
外部链接
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










