冒泡排序
| 冒泡排序 | |
|---|---|
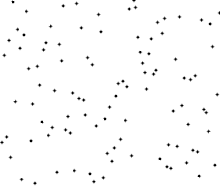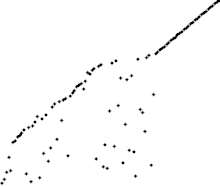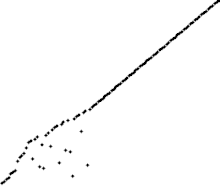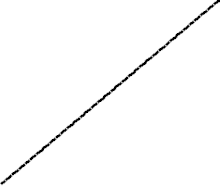 使用冒泡排序為一列數字進行排序的過程 | |
| 概况 | |
| 類別 | 排序算法 |
| 資料結構 | 數組 |
| 复杂度 | |
| 平均時間複雜度 | |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | |
| 最优时间复杂度 | |
| 空間複雜度 | 总共,需要辅助空间 |
| 最佳解 | No |
| 相关变量的定义 | |
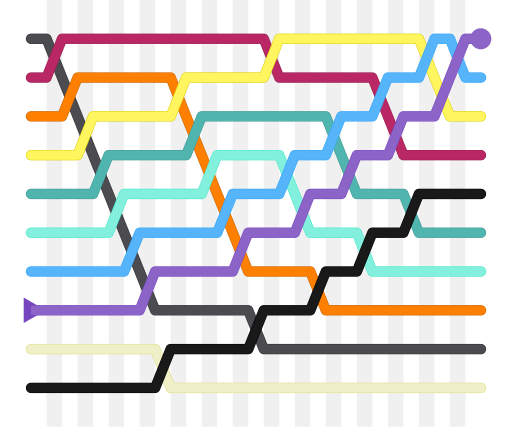
冒泡排序(英語:Bubble Sort)又稱為泡式排序,是一種簡單的排序算法。它重複地走訪過要排序的數列,一次比較兩個元素,如果它們的順序錯誤就把它們交換過來。走訪數列的工作是重複地進行直到沒有再需要交換,也就是說該數列已經排序完成。這個算法的名字由來是因為越小的元素會經由交換慢慢「浮」到數列的頂端。
冒泡排序對個項目需要O()的比較次數,且可以原地排序。儘管這個演算法是最簡單瞭解和實作的排序算法之一,但它對於包含大量的元素的數列排序是很沒有效率的。
冒泡排序是與插入排序擁有相等的漸近時間複雜度,但是兩種算法在需要的交換次數卻很大地不同。在最壞的情況,冒泡排序需要次交換,而插入排序只要最多交換。冒泡排序的實現(類似下面)通常會對已經排序好的數列拙劣地執行(),而插入排序在這個例子只需要個運算。因此很多現代的演算法教科書避免使用冒泡排序,而用插入排序取代之。冒泡排序如果能在內部迴圈第一次執行時,使用一個旗標來表示有無需要交換的可能,也可以把最優情況下的複雜度降低到。在這個情況,已經排序好的數列就無交換的需要。若在每次走訪數列時,把走訪順序反過來,也可以稍微地改進效率。有時候稱為雞尾酒排序,因為演算法會從數列的一端到另一端之間穿梭往返。
冒泡排序演算法的運作如下:
- 比較相鄰的元素。如果第一個比第二個大,就交換它們兩個。
- 對每一對相鄰元素作同樣的工作,從開始第一對到結尾的最後一對。這步做完後,最後的元素會是最大的數。
- 針對所有的元素重複以上的步驟,除了最後一個。
- 持續每次對越來越少的元素重複上面的步驟,直到沒有任何一對數字需要比較。
由於它的簡潔,冒泡排序通常被用來對於程式設計入門的學生介紹演算法的概念。
伪代码
function bubble_sort (array, length) {
var i, j;
for(i from 0 to length-1){
for(j from 0 to length-2-i){
if (array[j] > array[j+1])
swap(array[j], array[j+1])
}
}
}
函數 泡沫排序 輸入 一個陣列名稱為array 其長度為length
i 從 0 到 (length - 1)
j 從 0 到 (length - 2 - i)
如果 array[j] > array[j + 1]
交換 array[j] 和 array[j + 1] 的值
如果結束
j迴圈結束
i迴圈結束
函數結束
助记码
i∈[0,N-1) //循环N-1遍
j∈[0,N-1-i) //每遍循环要处理的无序部分
swap(j,j+1) //两两排序(升序/降序)
實作範例
C语言
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define ARR_LEN 255 /* 數組長度上限 */
#define elemType int /* 元素類型 */
/* 泡沫排序 */
/* 1. 從當前元素起,向後依次比較每一對相鄰元素,若逆序則互換 */
/* 2. 對所有元素均重複以上步驟,直至最後一個元素 */
/* elemType arr[]: 排序目標數組; int len: 元素個數 */
void bubbleSort (int arr[], int len)
{
int i, j,temp;
_Bool exchanged = true;
for (i=0; exchanged && i<len-1; i++){ /* 外迴圈為排序趟數,len個數進行len-1趟,只有交換過,exchanged值為true才有必要執行迴圈,否則exchanged值為false不執行迴圈 */
exchanged = false;
for (j=0; j<len-1-i; j++)
{ /* 內迴圈為每趟比較的次數,第i趟比較len-i次 */
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1])
{ /* 相鄰元素比較,若逆序則互換(升序為左大於右,逆序反之) */
temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
exchanged = true; /*只有數值互換過, exchanged才會從false變成true,否則數列已經排序完成,exchanged值仍然為false,沒必要排序 */
}
}
}
}
int main (void) {
int arr[ARR_LEN] = {3,5,1,-7,4,9,-6,8,10,4};
int len = 10;
int i;
bubbleSort (arr, len);
for (i=0; i<len; i++)
printf ("%d\t", arr[i]);
putchar ('\n');
return 0;
}
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T> //整数或浮点数皆可使用,若要使用类(class)或结构体(struct)时必须重载大于(>)运算符
void bubble_sort(T arr[], int len) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
for (j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1])
swap(arr[j], arr[j + 1]);
}
int main() {
int arr[] = { 61, 17, 29, 22, 34, 60, 72, 21, 50, 1, 62 };
int len = (int) sizeof(arr) / sizeof(*arr);
bubble_sort(arr, len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << arr[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
float arrf[] = { 17.5, 19.1, 0.6, 1.9, 10.5, 12.4, 3.8, 19.7, 1.5, 25.4, 28.6, 4.4, 23.8, 5.4 };
len = (float) sizeof(arrf) / sizeof(*arrf);
bubble_sort(arrf, len);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
cout << arrf[i] << ' '<<endl;
return 0;
}
C#
private int[] BubbleSort(int[] array)
{
var temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.Length; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < array.Length - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (array[j] > array[j + 1])
{
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return array;
}
JAVA
private int[] bubbleSort(int[] array) {
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
boolean Flag = false; // 是否发生交换。没有交换,提前跳出外层循环
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
Flag = true;
}
}
if (!Flag)
{
break;
}
}
return array;
}
Ruby
class Array
def bubble_sort!
for i in 0...(size - 1)
for j in 0...(size - i - 1)
self[j], self[j + 1] = self[j + 1], self[j] if self[j] > self[j + 1]
end
end
self
end
end
puts [22, 34, 3, 32, 82, 55, 89, 50, 37, 5, 64, 35, 9, 70].bubble_sort!
JavaScript
Array.prototype.bubble_sort = function() {
var i, j, temp;
for (i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++)
for (j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j++)
if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) {
temp = this[j];
this[j] = this[j + 1];
this[j + 1] = temp;
}
return this;
};
var num = [22, 34, 3, 32, 82, 55, 89, 50, 37, 5, 64, 35, 9, 70];
num.bubble_sort();
for (var i = 0; i < num.length; i++)
document.body.innerHTML += num[i] + " ";
Pascal
輸入:(在程式同目錄下的文本文件:input.txt)
一行:等待排序的數(用空格隔開);
實例:194 638 124 482 469 245 852 294 484 243 623
輸出:(在程式同目錄下的文本文件:output.txt)
一行:已經排好的數(從小到大);
實例:124 194 243 245 294 469 482 484 623 638 852
procedure swap(j:longint); //交換過程
begin
a[j]:=a[j] xor a[j+1];
a[j+1]:=a[j] xor a[j+1];
a[j]:=a[j] xor a[j+1];
end;
procedure bubble_sort; //排序過程
var
i,j:longint;
flag:boolean; //flag標誌:若一次排序未發現數據交換,則說明數據已經有序,可以結束排序過程
begin
for i:=n-1 downto 1 do
begin
flag:=true;
for j:=1 to i do
begin
if a[j]>a[j+1] then
begin
swap(j);
flag:=false;
end;
end;
if flag then exit;
end;
end;
Python
def bubble_sorted(iterable):
new_list = list(iterable)
list_len = len(new_list)
for i in range(list_len-1):
for j in range(list_len - i - 1):
if new_list[j] > new_list[j + 1]:
new_list[j], new_list[j + 1] = new_list[j + 1], new_list[j]
return new_list
范例:
testlist = [27, 33, 28, 4, 2, 26, 13, 35, 8, 14]
print('sorted:', bubble_sorted(testlist))
輸出:
sorted: [2, 4, 8, 13, 14, 26, 27, 28, 33, 35]
Scratch
VB.NET
'泡沫排序由大到小的程式,預先產生一儲存亂數內容的陣列B,使用中斷點check,
'switch 為自定兩數交換的sub
Dim i, j, count As Integer
For i = 0 To UBound(b) - 1
Dim check As Boolean = False '進入排序後設定一布林變數令其初值為false
For j = 0 To UBound(b) - 1 - i
If b(j) < b(j + 1) Then switch(b(j), b(j + 1))
check = True '進行檢查程序,若符合交換條件即進行兩數值交換(呼叫sub程序) 並於交換後
'將check的值變更為true(表示有進行交換動作,則此數列尚未呈現最終排列序),
'離開本層for迴圈後再度將check值重設成false
count += 1
Next
If check = False Then Exit For '檢查進入迴圈後是否進行過數值交換,若check值為false,
'則表示排序進行到此時所有數列的值已呈現期望中的順序,
'因此尚未進行完的排序檢查動作可提早結束以提升效率。
Next
MsgBox("共經過了" & count & "次排序")
'泡沫排序由小到大的程式
Dim i, j, count As Integer
Dim check As Boolean
For i = 0 To UBound(b) - 1
check=false
For j = 0 To UBound(b) - 1 - i
If b(j) > b(j + 1) Then switch(b(j), b(j + 1))
count += 1
check = True
Next
If chk = False Then Exit For
Next
MsgBox("共經過了" & count & "次的排序")
'兩數值交換程式
Private Sub switch(ByRef a as integer, ByRef b as integer)
Dim c As Integer
c = a
a = b
b = c
End Sub
PHP
function swap(&$x, &$y) {
$t = $x;
$x = $y;
$y = $t;
}
function bubble_sort(&$arr) {//php的陣列視為基本型別,所以必須用傳參考才能修改原陣列
for ($i = 0; $i < count($arr) - 1; $i++)
for ($j = 0; $j < count($arr) - 1 - $i; $j++)
if ($arr[$j] > $arr[$j + 1])
swap($arr[$j], $arr[$j + 1]);
}
$arr = array(21, 34, 3, 32, 82, 55, 89, 50, 37, 5, 64, 35, 9, 70);
bubble_sort($arr);
for ($i = 0; $i < count($arr); $i++)
echo $arr[$i] . ' ';
Rust
pub fn bubble_sort(a: &mut[i32]){
for i in 0..a.len() {
for j in i..a.len() {
if a[i] > a[j] {
a.swap(i, j);
}
}
}
}
调用:
let mut a = [5,4,7,1,9];
bubble_sort(&mut a);
println!("{:?}", a);
Go
// BubbleSort 冒泡排序. data必须实现sort包中的Interface接口
func BubbleSort(data sort.Interface) {
n := data.Len()
for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {
isChanged := false
for j := 0; j < n-1-i; j++ {
if data.Less(j, j+1) {
data.Swap(j, j+1)
isChanged = true
}
}
if !isChanged {
break
}
}
}
调用:
// declare a array
// this array must implenet sort.Inerface
data := sort.IntSlice{22, 34, 3, 40, 18, 4}
BubbleSort(data)
Objective-C
- (NSArray*) bubbleSort: (NSArray *) unsortedArray {
if (unsortedArray.count <= 1) {
return unsortedArray;
}
NSMutableArray *sortedArray = [unsortedArray mutableCopy];
for (int i = 0; i < sortedArray.count-1; i++) {
BOOL exchanged = NO;
for (int j = 0; j< sortedArray.count-1-i; j++) {
if ([sortedArray[j] integerValue] > [sortedArray[j+1] integerValue]) {
[sortedArray exchangeObjectAtIndex:j withObjectAtIndex:j+1];
exchanged = YES;
}
}
if (!exchanged) {
break;
}
}
return [sortedArray copy];
}
Swift
func bubbleSort(unsortedArray: inout [Int]){
guard unsortedArray.count > 1 else{
return
}
for i in 0 ..< unsortedArray.count-1 {
var exchanged = false
for j in 0 ..< unsortedArray.count-1-i {
if unsortedArray[j] > unsortedArray[j+1] {
unsortedArray.swapAt(j, j+1)
exchanged = true
}
}
if !exchanged {
break
}
}
}
// Test
var list = [2, 3, 5, 7, 4, 8, 6 ,10 ,1, 9]
print(list)
bubbleSort(unsortedArray: &list)
print(list)
Shell
#/bin/bash
read -p "Please enter a sequence: " -a num
for ((i=0;i<$[${#num[*]}-1];i++));do
for((j=0;j<$[$[${#num[*]}-1]-$i];j++));do
if [ ${num[$j]} -gt ${num[$[$j+1]]} ];then
A=${num[$j]}
num[$j]=${num[$[$j+1]]}
num[$[$j+1]]=$A
fi
done
done
echo ${num[*]}
IDL
FUNCTION BubbleSort, arr
FOR i = 0, N_ELEMENTS(arr) - 2 DO BEGIN
FOR j = i + 1, N_ELEMENTS(arr) - 1 DO BEGIN
IF arr[i] GT arr[j] THEN BEGIN
temp = arr[i] & arr[i] = arr[j] & arr[j] = temp
ENDIF
ENDFOR
ENDFOR
RETURN, arr
END
Julia (程式語言)
function BubbleSort(A)
n = length(A)
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:(n-i)
if(A[j]>A[j+1])
A[j+1],A[j] = A[j],A[j+1]
end
end
end
return A
end
# Main Code
A = [16,586,1,31,354,43,3]
print(A) # Original Array
print(BubbleSort(A)) # Bubble Sort Array
外部連結
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.







