หน่วยไต
| หน่วยไต (Nephron) | |
|---|---|
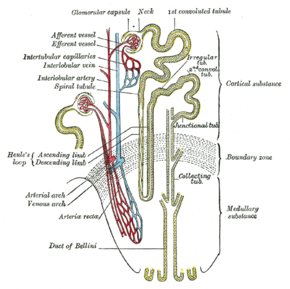 ภาพหน่วยไต(ภาพนี้ไม่มีจักซ์ตาโกลเมอรูลาร์ แอพพาราตัส) | |
| รายละเอียด | |
| คัพภกรรม | Metanephric blastema (intermediate mesoderm) |
| ตัวระบุ | |
| ภาษาละติน | nephroneum |
| MeSH | D009399 |
| FMA | 17640 |
| อภิธานศัพท์กายวิภาคศาสตร์ | |
หน่วยไต (อังกฤษ: nephron) เป็นโครงสร้างพื้นฐานและหน่วยทำงานพื้นฐานของไต มีหน้าที่หลักคือควบคุมสมดุลของสารน้ำและสารต่างๆ ในร่างกาย เช่นโซเดียม ผ่านการกรองเลือดที่ผ่านหน่วยไต ดูดกลับสารที่ต้องการ และขับสารที่ไม่ต้องการทิ้งผ่านทางปัสสาวะ หน้าที่ของหน่วยไตนี้มีความสำคัญอย่างยิ่งต่อการทำงานของร่างกาย ซึ่งจะถูกควบคุมโดยระบบต่อมไร้ท่อผ่านทางฮอร์โมนต่างๆ เช่น ฮอร์โมนต้านการขับปัสสาวะ อัลโดสเตอโรน และพาราไทรอยด์ เป็นต้น[1]
ไตปกติข้างหนึ่งของมนุษย์จะมีหน่วยไตอยู่ประมาณ 800,000 ถึง 1.5 ล้านหน่วยไต[2]
กายวิภาค
[แก้]โครงสร้างของ เนพฟรอน
โกลเมอรูลัส (glomerulus)
[แก้]เป็นกลุ่มเส้นเลือดฝอยที่นำสารมากรองออก มีลักษณะเป็นร่างแหสานกัน
โบว์แมนแคปซูล
[แก้]เป็นส่วนของท่อของหลอดไตที่พองเป็นกระเปาะ คล้ายด้าย มีโกลเมอรูลัสอยู่ข้างใน
ท่อของหน่วยไต
[แก้]อยู่ต่อจากโบว์แมนแคปซูล มี 3 ส่วนใหญ่ๆ
ท่อขดส่วนต้น
[แก้]เกิดการดูดสารเข้ากระแสเลือดมากที่สุด มีไมโทคอนเดรียเป็นจำนวนมาก เพื่อใช้เป็นพลังงานในการดูดสาร
ห่วงเฮนเล
[แก้]เป็นท่อขนาดเล็กโค้ง เป็นรูปตัวU ใช้ในการดูดสารกลับเช่นกัน มีไมโทรคอนเดรียน้อยกว่าท่อส่วนต้น
ท่อขดส่วนท้าย
[แก้]มีลักษณะเป็นท่อปิดของกรวยไต มีกรองแล้วส่งไปกระเพาะปัสสาวะ
การทำงาน
[แก้]การทำงานเกือบทั้งหมดของไตเกิดขึ้นในหน่วยไต หน้าที่เหล่านี้ส่วนใหญ่เกี่ยวข้อกับการดูดซึมกลับ (reabsorption) และการหลั่ง (secretion) ของสารละลายต่างๆ ทั้งไอออน (เช่น โซเดียม), คาร์โบไฮเดรต (เช่น น้ำตาลกลูโคส) และกรดอะมิโน (เช่น กลูตาเมต) คุณสมบัติของเซลล์ที่บุท่อหน่วยไตในตำแหน่งต่างๆ จะมีความแตกต่างกันมาก ดังนั้นตำแหน่งต่างๆ ของหน่วยไตจึงมีหน้าที่เฉพาะ
อ้างอิง
[แก้]- ↑ Maton, Anthea (1993). Human Biology and Health. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, USA: Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-981176-1.
((cite book)): ไม่รู้จักพารามิเตอร์|coauthors=ถูกละเว้น แนะนำ (|author=) (help) - ↑ Guyton, Arthur C.; Hall, John E. (2006). Textbook of Medical Physiology. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. p. 310. ISBN 0-7216-0240-1.
((cite book)): CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (ลิงก์)
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
