测度具有单调性 ,如果集合 A是集合B的子集 ,那么集合A的测度小于或等于集合B的测度。此外空集 的测度为0。例如体积(物体所占据的空间的大小)就是一种测度。 在数学 中,测度 是一種將几何空間 的度量 (长度 、面积 、体积 )和其他常见概念(如大小 、质量 和事件 的概率 )廣義化 後產生的概念。传统的黎曼积分 是在区间 上进行的,為了把积分推广到更一般的集合上,人們就发展出测度的概念。一个特别重要的例子是勒贝格测度 ,它從
n
{\displaystyle n}
R
n
{\displaystyle {\mathbb {R} }^{n))
研究測度的學問被統稱為测度论 ,因為指定的數值通常是非負实数 ,所以测度论通常會被視為实分析 的一个分支,它在数学分析 和概率论 有重要的地位。
正式定义
定義 —
(
X
,
Σ
)
{\displaystyle (X,\,\Sigma )}
可测空间 ,函数
μ
:
Σ
→
[
0
,
∞
)
{\displaystyle \mu :\Sigma \to [0,\,\infty )}
μ
(
∅
)
=
0
{\displaystyle \mu (\varnothing )=0}
可数可加性 (
σ
{\displaystyle \sigma }
序列
{
E
n
∈
Σ
}
n
∈
N
{\displaystyle \{E_{n}\in \Sigma \}_{n\in \mathbb {N} ))
正整數
i
≠
j
{\displaystyle i\neq j}
E
i
∩
E
j
=
∅
{\displaystyle E_{i}\cap E_{j}=\varnothing }
μ
(
⋃
n
∈
N
E
n
)
=
∑
n
=
1
∞
μ
(
E
n
)
{\displaystyle \mu \left(\bigcup _{n\in \mathbb {N} }E_{n}\right)=\sum _{n=1}^{\infty }\mu (E_{n})}
那
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
Σ
{\displaystyle \Sigma }
非負測度 ,或簡稱為測度 。為了敘述簡便起見,也可稱
(
X
,
Σ
,
μ
)
{\displaystyle (X,\,\Sigma ,\,\mu )}
测度空间 。
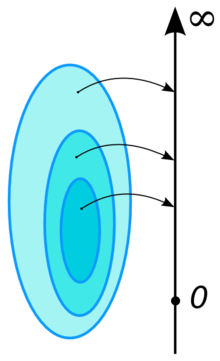
直觀上,測度是「體積」的推廣;因為空集合的「體積」當然為零,而且互相獨立的一群(可數個)物體,總「體積」當然要是所有物體「體積」直接加總(的極限)。而要定義「體積」,必須先要決定怎樣的一群子集合,是「可以測量的」,詳細請見σ
如果將
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
複數 ,也就是說
μ
:
Σ
→
C
{\displaystyle \mu :\Sigma \to \mathbb {C} }
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
複數測度 。[1]
定義的分歧
若照著上述定義,根據可数可加性,不少母集合本身的測度值會變成无穷大 (如對
R
n
{\displaystyle {\mathbb {R} }^{n))
勒贝格测度 ),所以實際上不存在。但某些書籍[2] 无穷大 視為一個數,而容許測度取值為無窮大;這樣定義的書籍,會把只容許有限实数 值的測度稱為(非負)有限測度 。但這樣"定義",會造成可數可加性與數列收斂 的定義產生矛盾。
所以要延續體積是一種"度量"的這種直觀概念(也就是嚴謹的定義勒贝格测度 ),那就必須把σ 半集合環 前測度
更進一步的,如果對測度空間
(
X
,
Σ
,
μ
)
{\displaystyle (X,\,\Sigma ,\,\mu )}
X
{\displaystyle X}
Σ
{\displaystyle \Sigma }
{
E
n
∈
Σ
}
n
∈
N
{\displaystyle \{E_{n}\in \Sigma \}_{n\in \mathbb {N} ))
并集 :
X
=
⋃
n
∈
N
E
n
{\displaystyle X=\bigcup _{n\in \mathbb {N} }E_{n))
且
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
μ
{\displaystyle \mu }
σ-有限测度 。
性质
单调性
测度
μ
{\displaystyle \mu \ }
单调性 :
若
E
1
{\displaystyle E_{1}\ }
E
2
{\displaystyle E_{2}\ }
E
1
⊆
E
2
{\displaystyle E_{1}\subseteq E_{2))
μ
(
E
1
)
≤
μ
(
E
2
)
{\displaystyle \mu (E_{1})\leq \mu (E_{2})}
可数个可测集 的并集的测度
若
E
1
,
E
2
,
E
3
⋯
{\displaystyle E_{1},E_{2},E_{3}\cdots }
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}\ }
μ
(
⋃
i
=
1
∞
E
i
)
≤
∑
i
=
1
∞
μ
(
E
i
)
{\displaystyle \mu (\bigcup _{i=1}^{\infty }E_{i})\leq \sum _{i=1}^{\infty }\mu (E_{i})}
如果还满足并且对于所有的
n
{\displaystyle n\ }
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}\ }
E
n
+
1
{\displaystyle E_{n+1}\ }
极限式 成立:
μ
(
⋃
i
=
1
∞
E
i
)
=
lim
i
→
∞
μ
(
E
i
)
.
{\displaystyle \mu \left(\bigcup _{i=1}^{\infty }E_{i}\right)=\lim _{i\to \infty }\mu (E_{i}).}
可数个可测集 的交集的测度
若
E
1
,
E
2
,
⋯
{\displaystyle E_{1},E_{2},\cdots }
n
{\displaystyle n\ }
E
n
+
1
{\displaystyle E_{n+1}\ }
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}\ }
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}\ }
交集 是可测的。进一步说,如果至少一个
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}\ }
有限 ,则有极限:
μ
(
⋂
i
=
1
∞
E
i
)
=
lim
i
→
∞
μ
(
E
i
)
{\displaystyle \mu (\bigcap _{i=1}^{\infty }E_{i})=\lim _{i\to \infty }\mu (E_{i})}
如若不假设至少一个
E
n
{\displaystyle E_{n}\ }
n
∈
N
{\displaystyle n\in \mathbb {N} }
E
n
=
[
n
,
∞
)
⊆
R
{\displaystyle E_{n}=[n,\infty )\subseteq \mathbb {R} }
这裡,全部集合都具有无限测度,但它们的交集是空集。
完备性
直觀上,因為測度的單調性,只要包含於零測集的集合,也「應該」是零測集,完備測度的定義體現了這個直觀的想法。更進一步的,任意测度可以按如下的定理擴展为完备测度:[3]
定理 —
(
X
,
Σ
,
μ
)
{\displaystyle (X,\,\Sigma ,\,\mu )}
测度空间 ,若取:
Σ
⋆
:=
{
S
|
(
S
⊆
X
)
∧
(
∃
A
)
(
∃
B
)
{
(
A
,
B
∈
Σ
)
∧
(
A
⊆
S
⊆
B
)
∧
[
μ
(
B
−
A
)
=
0
]
}
}
{\displaystyle \Sigma ^{\star }:={\bigg \{}S\,{\bigg |}\,(S\subseteq X)\wedge (\exists A)(\exists B)\{(A,\,B\in \Sigma )\wedge (A\subseteq S\subseteq B)\wedge [\mu (B-A)=0]\}{\bigg \))}
那
Σ
⋆
{\displaystyle \Sigma ^{\star ))
Σ-代数 ,此時若定義:
μ
⋆
:=
{
⟨
S
,
r
⟩
|
(
S
⊆
X
)
∧
(
∃
A
)
(
∃
B
)
{
(
A
,
B
∈
Σ
)
∧
(
A
⊆
S
⊆
B
)
∧
[
μ
(
B
−
A
)
=
0
]
∧
[
r
=
μ
(
A
)
]
}
}
{\displaystyle \mu ^{\star }:={\bigg \{}\langle S,\,r\rangle \,{\bigg |}\,(S\subseteq X)\wedge (\exists A)(\exists B)\{(A,\,B\in \Sigma )\wedge (A\subseteq S\subseteq B)\wedge [\mu (B-A)=0]\wedge [r=\mu (A)]\}{\bigg \))}
那
μ
⋆
{\displaystyle \mu ^{\star ))
Σ
⋆
{\displaystyle \Sigma ^{\star ))
(
∀
S
∈
Σ
)
[
μ
⋆
(
S
)
=
μ
(
S
)
]
{\displaystyle (\forall S\in \Sigma )[\mu ^{\star }(S)=\mu (S)]}
参考文献
R. M. Dudley, 2002. Real Analysis and Probability . Cambridge University Press.
D. H. Fremlin, 2000. Measure Theory
Paul Halmos , 1950. Measure theory . Van Nostrand and Co.M. E. Munroe, 1953. Introduction to Measure and Integration . Addison Wesley.
Shilov, G. E., and Gurevich, B. L., 1978. Integral, Measure, and Derivative: A Unified Approach , Richard A. Silverman, trans. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-63519-8 . Emphasizes the Daniell integral.


































![{\displaystyle \Sigma ^{\star }:={\bigg \{}S\,{\bigg |}\,(S\subseteq X)\wedge (\exists A)(\exists B)\{(A,\,B\in \Sigma )\wedge (A\subseteq S\subseteq B)\wedge [\mu (B-A)=0]\}{\bigg \))}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9350c6a61f8fd7a24dd49edf9e34693378da3b56)

![{\displaystyle \mu ^{\star }:={\bigg \{}\langle S,\,r\rangle \,{\bigg |}\,(S\subseteq X)\wedge (\exists A)(\exists B)\{(A,\,B\in \Sigma )\wedge (A\subseteq S\subseteq B)\wedge [\mu (B-A)=0]\wedge [r=\mu (A)]\}{\bigg \))}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/be8fc614426d1ecbc9ddff5def9aa67820318e31)

![{\displaystyle (\forall S\in \Sigma )[\mu ^{\star }(S)=\mu (S)]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/325507b5ac2f0a3638b210cbe92e19a0718d7abc)


![{\displaystyle \mu ([0,1])=1\ }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/585179716417be6cf5a170cb3d9654dfe6d3039e)


