桂花负蝽
| 桂花负蝽 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Kirkaldyia deyrollei | |
| 科学分类 | |
| 界: | 动物界 Animalia |
| 门: | 节肢动物门 Arthropoda |
| 纲: | 昆虫纲 Insecta |
| 目: | 半翅目 Hemiptera |
| 科: | 负蝽科 Belostomatidae |
| 属: | Kirkaldyia属 Kirkaldyia |
| 种: | 桂花负蝽 K. deyrollei
|
| 二名法 | |
| Kirkaldyia deyrollei | |
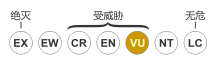
桂花负蝽(学名: Kirkaldyia deyrollei [注 1]),俗称水剪(台湾客家语)、水鲎(台湾话:tsuí-hāu),或称作狄氏大田鳖、日本大田鳖、田鳖、桂花蝉(在日本称高野圣)。本类昆虫为半翅目中最大的水生昆虫,牠也有食用性的用途,分布于热带、亚热带、温带地区,物种非常多样化[3][4],最大品种田鳖约4.7英寸(12cm),牠们在大部分国家内非常普遍常见[4],但在一些国家内数量大幅减少,在日本的保护状况受到威胁[5][6],已列入“易危物种”(VU)[1]。
外部型态
- 身体区分成头部、胸部与腹部三个部分。
- 胸部有一对特化呈镰刀状的前肢;胸部有两对足。
- 尾部末端有两根短呼吸管(可收缩)组成。
习性

成虫体长约5~8公分,体色接近暗褐色,为肉食性昆虫,性格凶猛,复眼发达,会利用特化的尖锐状镰刀前足捕捉猎物,其主食为青蛙、蝌蚪和鱼类,有时甚至会捕捉其他水生昆虫、福寿螺以及乌龟、蛇等爬行纲[7][8]、老鼠等小型哺乳类,水中体型比牠大的动物都有可能成为牠捕食的对象,在捕捉到猎物的同时,田鳖会迅速注入消化液腐蚀猎物内部并吸取的溶解后的体液,大田鳖的饮食偏好为蛙类和鱼类[9][10],前足上的勾爪亦可划伤、勾住猎物的皮肤,而中、后足为扁平状,为游泳足,而翅膀不常使用,不过飞行能力很强,因有趋光性,夜间会飞行到灯光明亮处。其天敌为鹭鸶等鸟类。
雌型个体较大、肥胖,达到6公分的雄性个体更是罕见。其最大个体产于南美洲,体长可达12公分以上。田鳖与红娘华有近亲关系[11],共同特征为手中具有特化的镰刀钳助于捕食猎物、同样为刺吸式口器进食。经常栖息于植被水域或稻田中水草较为茂密的静水区[12],并代表稻田的“环境指标生物”[13],可以用来测量水质的干净程度。当冬季到达时,田鳖会主要选择离水不远的陆地上草较茂密的地方、石头下过冬,少数会选择于水中生活缓慢的代谢并等待春天的到来。成虫一般在野外的寿命可达1年以上,不过在人工饲养的环境下也有达3年以上的例子,在繁殖季节时,通常田鳖于5、6月成熟,会大量出现,当雄虫找到适宜的对象后会拍动水波吸引雌虫的注意是否进行交配,交配后,雌虫产下多个卵形成块状产于离开水面的水草、树枝条上等等,产卵完后,雄虫将会担任守卫并保护卵块,并给予卵适当的水分,让卵助于孵化,经过几天的时间孵化后,会落入水中,开始展开生活,经过调查指出雄性个体的数量比例比雌性还高,是种成虫(雄性)皆有护卵行为的水生昆虫[14]。不过有些野外尚未交配的雌虫会使用前足破坏雄虫正在保护的卵块,借此使雄虫无法保护前任雌虫的卵块而放弃护卵的职责,迫使雄虫会与新的雌虫交配让新的雌虫来繁殖下一代,并重新转移担任护卵的职责。[12][15]
危害与濒危
在早期,在各个国家田鳖数量很多,以鱼池、水生生物栖息地出没,生物都难逃一劫,遭到牠们的猎食,已造成危害归为“害虫”[注 2],之后人们开始使用农药等等毒素侵害水源,也随着都市化,稻田、水域的消失,导致水质环境要求条件较高的牠们死亡[注 3],但也不只有牠们,包括其他的水生昆虫、生物也难逃,导致部分水生生物的危害至今[16]。
其他品种

世界上有很多种,目前已知确认的有20种,每种都是当地水生昆虫中的大型种。
- Lethocerus annvilipes:分布于南美洲的大型种,体长约9公分,但身体较细长一点、前足较小,当地约6、7、8月为繁殖季节,会大量飞向灯光区。
- Lethocerus americanus:体长约5至6公分[17],与台湾产的桂花负蝽相似。
- Belostoma grandis:分布于南美洲,是世界和半翅目中最大品种,其体长可达到10公分以上,与L.maximus相当,也一样在南美洲,牠可能是另一个独立的物种或与L.maximus同类。
- Lethocerus grisens:栖息于佛罗里达州,稍微比美国产的田鳖小些,约7公分左右。
- Lethocerus insulanus:栖息于澳大利亚东北部地区,特别是昆士兰州,还有新南威尔士州北部等地区,其他地区包括菲律宾和美拉尼西亚,和新喀里多尼亚和巴布亚新几内亚。[18]体长约6公分左右,生活在静止的淡水湖泊中。[19]
- Lethocerus indicus:印田鳖蝽,栖息于东南亚以及中国东南部、韩国、琉球群岛和新几内亚。[4]其中最大特征是头部到胸部有着一个“V”字斑纹线条,在日本冲绳县八重山群岛与那国岛也有分布,体长约6.5至8.5公分左右[4],比桂花负蝽稍大一些,成体的印度大田鳖在越南、泰国为一种非常受欢迎的菜肴[20],也会拿来制作成泰式辣椒酱等调味品。[21]
- Lethocerus maximus:分布于南美洲,与B.grandis同样可达到10公分以上,生活在环境丰富的水域,和其他田鳖一样雄虫会保护卵块。
- Lethocerus mericanus:分布于北美洲,体长和前足较小的品种。
- Lethocerus uhleri:于中美洲和北美洲发现的品种。[24]是小型种田鳖,体长约4.5公分左右,比起其他田鳖,体型非常的瘦。
- Hydrocyrinus属:世界有6到7种,和田鳖很相似的另一个物种,卵块和其他田鳖有些差异。
另见
备注
参考文献
- ^ 1.0 1.1 カメムシ目コオイムシ科 绝灭危惧II类(VU) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)(日语)
- ^ P. J. Perez-Goodwyn. Taxonomic revision of the subfamily Lethocerinae Lauck & Menke (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae). Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde. A (Biologie). 2006, 695: 1–71.
- ^ D. R. Lauck & A. Menke. The higher classification of the Belostomatidae (Hemiptera). Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 1961, 54: 644–657.
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 P. J. Perez-Goodwyn (2006). Taxonomic revision of the subfamily Lethocerinae Lauck & Menke (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae)". Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde. A (Biologie) 695: 1–71.
- ^ Hirai, T.; and Hidaka, K. (2002). Anuran-dependent predation by the giant water bug, Lethocerus deyrollei (Hemiptera: Belostomatidae), in rice fields of Japan. Ecological Research 17(6): 655-661.
- ^ Ohba, S. (2007). Notes on predators and their effect on the survivorship of the endangered giant water bug, Kirkaldyia (= Lethocerus) deyrolli (Heteroptera, Belostomatidae), in Japanese rice fields. Hydrobiologia 583(1): 377-381.
- ^ Ohba, S.; Izumi, Y.; and Tsumuki, H. (2012). Effect of loach consumption on the reproduction of giant water bug Kirkaldyia deyrolli: dietary selection, reproductive performance, and nutritional evaluation. Journal of Insect Conservation 16(6): 829-838.
- ^ BBC News (26 May 2011). Giant water bug photographed devouring baby turtle. (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) Retrieved 27 August 2014.
- ^ A. C. Huntley (1998). "Lethocerus americanus, the "toe biter"". Dermatology Online Journal 4 (2): 6.
- ^ 《昆虫入门》 (1998年)国际标准书号957-32-3486-6
- ^ 11.0 11.1 《虫志》MOOOK No.6 P90田鳖下战书 商鼎文化出版社 国际标准书号986-144-030-5
- ^ 12.0 12.1 Ichikawa, N. (1995) Male counterstrategy against infanticide of the female giant water bug Lethocerus deyrollei (Hemiptera: Belostomatidae). Journal of Insect Behavior 8:181-186.
- ^ 13.0 13.1 山と渓谷社“田んぼの生き物図鉴” (2013年3月5日初版第1刷発行 著者:内山りゅう、ISBN 978-4-635-06286-2) p.132
- ^ 《台湾昆虫记》 作者:潘建宏 撰文:廖智安 p279的昆虫分类与图鉴。大树文化出版社 国际标准书号957-8792-47-6
- ^ Ichikawa, N. (1991), Egg mass destroying and guarding behaviour of the giant water bug Lethocerus deyrollei Vuillefroy (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae). Journal of Ethology 9: 25-29.
- ^ 通霄 77歲老農轉做自然農法,守護夢幻水生昆蟲 大田鱉. 上下游News&Market. 2013-07-12 [2014-04-21]. (原始内容存档于2014-04-22).
- ^ P. J. Perez-Goodwyn (2006). Taxonomic revision of the subfamily Lethocerinae Lauck & Menke (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae)". Stuttgarter Beiträge zur Naturkunde. A (Biologie) 695: 1–71.
- ^ Species Lethocerus (Lethocerus) insulanus (Montandon, 1898) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆), Australian Faunal Directory, Department of the Environment, 30 November 2012.
- ^ Giant Water Bug (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆), Australian Museum.
- ^ 存档副本. [2007年10月30日]. (原始内容存档于2007年10月14日). - ThaiBugs.com
- ^ Chapter 24 SE Asia Thailand 互联网档案馆的存档,存档日期2012-02-23.
- ^ Lethocerus medius Report. Integrated Taxonomic Information System. [2018-05-06]. (原始内容存档于2021-05-09).
- ^ Grozeva, Snejana; Kuznetsova, Valentina; Simov, Nikolay; Langourov, Mario; Dalakchieva, Svetla. Sex chromosome pre-reduction in male meiosis of Lethocerus patruelis (Stål, 1854) (Heteroptera, Belostomatidae) with some notes on the distribution of the species. ZooKeys. 2013, 319: 119–135. ISSN 1313-2970. PMC 3764518
 . PMID 24039515. doi:10.3897/zookeys.319.4384.
. PMID 24039515. doi:10.3897/zookeys.319.4384.
- ^ Lethocerus uhleri Report. Integrated Taxonomic Information System. [2018-05-01]. (原始内容存档于2021-12-30).
外部链接
- タガメ Lethocerus deyrolli 保护状况 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)(多样性生物调查)
- 苹果调查:昆虫界猛禽 田鳖绝迹30年 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- 苹果调查:守护梦幻昆虫 种出田鳖米
- 昆虫界暖男爸爸 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
|
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.