Reakcja Schotten-Baumanna
Reakcja Schotten-Baumanna – reakcja chemiczna amin z chlorkami kwasowymi, której produktami są amidy. Reakcja została odkryta w 1883 roku przez chemików niemieckiego pochodzenia Carla Schottena i Eugena Baumanna[1][2].
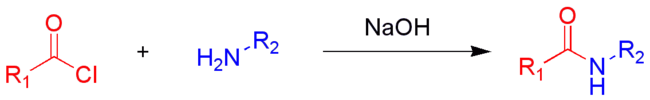
Czasami nazwą tą określa się także reakcję chlorków kwasowych z alkoholami, prowadzącą do powstania estrów.
Mechanizm
[edytuj | edytuj kod]Nukleofilowy atak aminy na karbonylowy atom węgla chlorku kwasowego prowadzi do powstania anionu chloru oraz sprotonowanego amidu. Następnie nieprzereagowana cząsteczka aminy deprotonuje amid, stając się niereaktywna wobec chlorku kwasowego. Dodany ekwiwalent zasady sodowej deprotonuje nieaktywną aminę, która reaguje z chlorkiem kwasowym zamykając cykl reakcji.

Reakcję Schotten-Baumanna często przeprowadza się w układzie dwufazowym (mówi się wówczas o warunkach reakcji Schotten-Baumanna). Zasadowa wodna faza neutralizuje kwaśną sól amoniową, a produkt pozostaje w fazie organicznej. Jako rozpuszczalnika organicznego najczęściej używa się chlorku metylenu, eteru dietylowego lub toluenu.
Zastosowania
[edytuj | edytuj kod]Reakcja Schotten-Baumanna bądź jej warunki są powszechnie stosowane w syntezie organicznej. Przykładowe procedury:
- synteza N-wanilinononanamidu, znanego jako syntetyczna kapsaicyna (1)
- synteza N-(3,4-dimetoksyfenyloetylo)benzamidu (2) z chlorku benzoilu i 2-(3,4-dimetoksyfenylo)etyloaminy
- synteza N-(1-fenyloetylo)acetamidu (3) przez acylowanie 1-fenyloetyloaminy chlorkiem acetylu lub bezwodnikiem octowym

Reakcja α-chloro chlorków kwasowych z estrami aminokwasów umożliwia syntezę łańcuchów peptydowych, znana jest jako synteza peptydów Fishera[3][4].
Przypisy
[edytuj | edytuj kod]- ↑ C. Schotten. Ueber die Oxydation des Piperidins. „Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft”. 17 (2), s. 2544–2547, 1884. DOI: 10.1002/cber.188401702178.
- ↑ E. Baumann. Ueber eine einfache Methode der Darstellung von Benzoësäureäthern. „Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft”. 19 (2), s. 3218–3222, 1886. DOI: 10.1002/cber.188601902348.
- ↑ Emil Fischer. Synthese von Polypeptiden. „Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft”. 36 (3), s. 2982–2992, 1903. DOI: 10.1002/cber.19030360356.
- ↑ Fischer Peptide Synthesis
Linki zewnętrzne
[edytuj | edytuj kod]Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
