Hypusine
| Hypusine | |
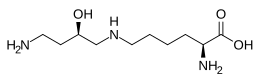 Structure de l'hypusine |
|
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | N6-[(2R)-4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl]- L-lysine |
| No CAS | |
| PubChem | 21878228 |
| ChEBI | 21858 |
| SMILES | |
| InChI | |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C10H23N3O3 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 233,307 9 ± 0,011 1 g/mol C 51,48 %, H 9,94 %, N 18,01 %, O 20,57 %, |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier |
|
L'hypusine est un acide aminé inhabituel présent chez tous les eucaryotes et les archées mais absent chez les bactéries. Son nom provient de sa structure, comprenant un résidu d'hydroxyputrescine lié à un résidu de lysine. La seule protéine connue contenant de l'hypusine est l'eIF5A (en) (facteur d'initiation eucaryotique (en) 5A) des eucaryotes, ainsi qu'une protéine voisine chez les archées[2].
Cette protéine est impliquée dans la biosynthèse des protéines en permettant la formation de la première liaison peptidique. La région environnant le résidu d'hypusine et très fortement conservée et est essentiellement au fonctionnement de l'eIF5A[3]. L'hypusine et l'eIF5A apparaissent donc indispensables à la viabilité et à la prolifération des cellules eucaryotiques.
L'hypusine est formée sur l'eIF5A par modification post-traductionnelle sur l'un des résidus de lysine. Deux enzymes interviennent dans ce processus :
- la désoxyhypusine synthase catalyse le clivage de la spermidine et le transfert de son résidu 4-aminobutyle sur le groupe ε-amine d'un résidu de lysine spécifique, ce qui forme de la désoxyhypusine et du 1,3-diaminopropane ;
- la désoxyhypusine hydroxylase conduit à la formation d'hypusine en introduisant un groupe hydroxyle sur le résidu de désoxyhypusine.
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Myung Hee Park, « The Post-Translational Synthesis of a Polyamine-Derived Amino Acid, Hypusine, in the Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 5A (eIF5A) », Journal of Biochemistry, vol. 139, no 2, , p. 161-169 (PMCID 2494880, lire en ligne) DOI 10.1093/jb/mvj034 ;
- (en) Veridiana S. P. Cano, Geoung A. Jeon, Hans E. Johansson, C. Allen Henderson, Jong-Hwan Park, Sandro R. Valentini, John W. B. Hershey et Myung Hee Park, « Mutational analyses of human eIF5A-1 – identification of amino acid residues critical for eIF5A activity and hypusine modification », FEBS Journal, vol. 275, no 1, , p. 44-58 (PMCID 2536608, lire en ligne) DOI 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.06172.x ;
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
