X染色體
| X染色體 | |
|---|---|
| 物種 | Homo sapiens |
| 基因數量 | 900-1200 |
X染色體(英語:X chromosome)是部分動物決定性別的染色體之一。它出現在X0性別決定系統和XY性別決定系統中。對一般人類來說,女性有兩條X染色體,男性X、Y染色體各有一條。
Hermann Henking發現了X染色體。
人類
在人類約20,000至25,000個基因之中,X染色體約有2,000個基因。
一般女性有兩條X染色體,其中一條會惰性化,變成巴爾體(Barr body),這個作用稱為X去活性(X inactivation)或里昂化作用(lyonization,以發現者Mary F. Lyon命名)。(參見:三色貓) 不論生物遺傳了幾個X染色體,都只有一個X染色體會活性化,其餘皆惰性化,使生物能正常發揮功能,並具有修復功能。
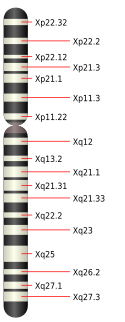
細胞遺傳帶
| Chr. | Arm[6] | Band[7] | ISCN start[8] |
ISCN stop[8] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[9] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | p | 22.33 | 0 | 323 | 1 | 4,400,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 22.32 | 323 | 504 | 4,400,001 | 6,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| X | p | 22.31 | 504 | 866 | 6,100,001 | 9,600,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 22.2 | 866 | 1034 | 9,600,001 | 17,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| X | p | 22.13 | 1034 | 1345 | 17,400,001 | 19,200,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 22.12 | 1345 | 1448 | 19,200,001 | 21,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| X | p | 22.11 | 1448 | 1577 | 21,900,001 | 24,900,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 21.3 | 1577 | 1784 | 24,900,001 | 29,300,000 | gpos | 100 |
| X | p | 21.2 | 1784 | 1862 | 29,300,001 | 31,500,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 21.1 | 1862 | 2120 | 31,500,001 | 37,800,000 | gpos | 100 |
| X | p | 11.4 | 2120 | 2430 | 37,800,001 | 42,500,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 11.3 | 2430 | 2624 | 42,500,001 | 47,600,000 | gpos | 75 |
| X | p | 11.23 | 2624 | 2948 | 47,600,001 | 50,100,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 11.22 | 2948 | 3129 | 50,100,001 | 54,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| X | p | 11.21 | 3129 | 3206 | 54,800,001 | 58,100,000 | gneg | |
| X | p | 11.1 | 3206 | 3297 | 58,100,001 | 61,000,000 | acen | |
| X | q | 11.1 | 3297 | 3491 | 61,000,001 | 63,800,000 | acen | |
| X | q | 11.2 | 3491 | 3620 | 63,800,001 | 65,400,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 12 | 3620 | 3827 | 65,400,001 | 68,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| X | q | 13.1 | 3827 | 4137 | 68,500,001 | 73,000,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 13.2 | 4137 | 4292 | 73,000,001 | 74,700,000 | gpos | 50 |
| X | q | 13.3 | 4292 | 4447 | 74,700,001 | 76,800,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 21.1 | 4447 | 4732 | 76,800,001 | 85,400,000 | gpos | 100 |
| X | q | 21.2 | 4732 | 4809 | 85,400,001 | 87,000,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 21.31 | 4809 | 5107 | 87,000,001 | 92,700,000 | gpos | 100 |
| X | q | 21.32 | 5107 | 5184 | 92,700,001 | 94,300,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 21.33 | 5184 | 5430 | 94,300,001 | 99,100,000 | gpos | 75 |
| X | q | 22.1 | 5430 | 5701 | 99,100,001 | 103,300,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 22.2 | 5701 | 5843 | 103,300,001 | 104,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| X | q | 22.3 | 5843 | 6050 | 104,500,001 | 109,400,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 23 | 6050 | 6322 | 109,400,001 | 117,400,000 | gpos | 75 |
| X | q | 24 | 6322 | 6619 | 117,400,001 | 121,800,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 25 | 6619 | 7059 | 121,800,001 | 129,500,000 | gpos | 100 |
| X | q | 26.1 | 7059 | 7253 | 129,500,001 | 131,300,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 26.2 | 7253 | 7395 | 131,300,001 | 134,500,000 | gpos | 25 |
| X | q | 26.3 | 7395 | 7602 | 134,500,001 | 138,900,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 27.1 | 7602 | 7808 | 138,900,001 | 141,200,000 | gpos | 75 |
| X | q | 27.2 | 7808 | 7886 | 141,200,001 | 143,000,000 | gneg | |
| X | q | 27.3 | 7886 | 8145 | 143,000,001 | 148,000,000 | gpos | 100 |
| X | q | 28 | 8145 | 8610 | 148,000,001 | 156,040,895 | gneg |
疾病
因X染色體數目異常而出現的疾病:
- X-三體:女性有三條X染色體。她們發展較遲緩(但可透過後天培養而糾正),平均智力為90,較正常的100為低。她們能正常生育。[1]在罕見的情況下會出現如XXXX或XXXXX。
- 克氏综合症:男性有兩條X染色體。他們的睪酮水平可能較低,胸部發育接近女性。罕見的情況下會出現XXXY或XXXXY。
- 透納氏症(Turner syndrome):女性只有一條X染色體。她們身材較矮小,性功能不能正常發展。
遺傳病

X性聯隱性遺傳病是指一個人所有的X染色體都有帶病基因時才會發生的疾病。男性患上這些疾病的機會都比女性高,因為男性只有一條X染色體,而女性有兩條。若女性其中一條有帶病基因,另一條仍可以發揮作用,但可能也會有較輕微的症狀出現,因為在每個細胞內去活性化的X染色體都是隨機決定的,若在負責帶病基因相關功能的細胞內去活性化的為帶正常基因的染色體,就會有輕微的症狀出現,例如帶有色盲致病基因的女性,若在視網膜組織內有較多的帶正常基因X染色體不活化,則該女性的辨色力會比基因型完全正常的女性要差。
若以XB表示正常基因,以Xb表示帶病基因,則男性病者表示為XbY,辨色能力正常者為XBY;女性病者表示為XbXb,帶因者為XBXb,功能正常亦非帶因者為XBXB。排除子代發生基因突變的情況下,子代與父母辨色能力的關係如下:
- 父母均為病者(XbY,XbXb)
- 兒子為XbY,女兒為XbXb,即子代都是病者。
- 父親正常,母親為病者(XBY,XbXb)
- 兒子為XbY,女兒為XBXb,即兒子都是病者,女兒為帶因者。
- 父親為病者,母親正常(兩種情況)
- 父親為XbY,母親為XBXB
- 兒子為XBY,女兒為XbXB,即兒子正常,女兒為帶因者。
- 父親為XbY,母親為XBXb
- 兒子XBY或XbY,女兒為XBXb或XbXb,即兒子有50%的概率為病者,女兒必為帶因者,而其中有50%的機率為病者。
- 父親為XbY,母親為XBXB
- 父母均正常(兩種情況)
- 父親為XBY,母親為XBXB
- 兒子為XBY,女兒為XBXB,即子代都正常。
- 父親為XBY,母親為XBXb
- 兒子為XBY或XbY,女兒為XBXB或XBXb,即兒子有50%的概率為病者,女兒有50%的概率為帶因者。
- 父親為XBY,母親為XBXB
常見的X性聯隱性遺傳病有:
- 重症肌無力
- 血小板減少症
- 痛風
- SCID(先天性免疫缺乏症、泡泡兒)
- 眼球白化症
- 裂顎
- 肌肉萎縮症
- 血友病
- 色盲
- ALD(腎上腺腦白質退化症)
- G6PD(蠶豆症)
- XLSA(含鐵母細胞性貧血的一種)
- X染色體易裂症
- 法布瑞氏症
- 愛伯症候群
此外,亦有顯性遺傳病,已知文獻中,此遺傳類型非常稀少。(父母任何一方為病患者便有可能傳到後代)如:
註釋
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ^ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature. ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. 2013. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7.
- ^ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images. 2012: 276–282 [2020-02-10]. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. (原始内容存档于2021-03-11).
|journal=被忽略 (帮助) - ^ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ^ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ^ 8.0 8.1 These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ^ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
參見
- ZC4H2缺乏症(ZC4H2 deficiency)
外部連結
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.