易用度
定義
[編輯]| 「 | 」 |
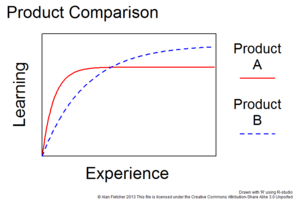
喺最簡化嗰種情況下,易用度可以用學習曲線(learning curve)嘅概念嚟想像。學習曲線係心理學同相關領域上用嚟模擬學習現象嘅一種數學模型:想像家陣有個人一路係噉做工作 做一段時間,正常嚟講,隨住時間過去,佢喺工作 上嘅表現正常嚟講會愈嚟愈好(做得愈嚟愈熟手),並且去到某一個點因為受試者技術去到最高點而變平;如果用 Y 軸做嗰個人喺工作 上嘅表現、X 軸做時間,就會畫出一條 Y 值隨時間上升嘅線,呢條就係嗰嗰個人喺工作 上嘅學習曲線,即係好似[2]:
- ;
當中 係喺工作 上嘅表現(一個理論上會隨住學習而數值下降嘅指標); 係經驗(或者時間); 係指第一吓工作嘅表現;而 呢個參數()會反映個工人嘅學習率(learning rate)。而家假想 係「使用一隻軟件」-如果一隻軟件對用家嚟講容易學識點用,噉用家喺使用隻軟件上嘅學習曲線應該會比較快到達平嘅最高點[3][4]:p. 2。
處理器模型
[編輯]易用度分析嘅其中一個最重要部份係考慮用家所做嘅認知過程:人類處理器模型(human processor model)係易用度分析上成日用嘅一個理論模型,主要攞嚟估計一位用家做某一樣認知作業(例如係撳某一個掣)要用幾耐嘅時間;根據呢個模型,人喺做認知作業嗰陣會經過一柞基本步驟,包括咗
- 用感官感知外界資訊並且理解自己周圍發生緊啲乜嘢事(perceptual subsystem)、
- 用工作記憶同長期記憶等嘅記憶功能整合手上嘅資訊(cognitive subsystem)同埋
- 用資訊整合得出嘅結果控制身體做出適當嘅郁動(motor subsystem);
即係好似下圖噉[5]:


人類處理器模型喺易用度分析上相當有用。例:設計者家陣想設計網購網站,佢哋用心理實驗嘅方法知道咗,用家對眼望勻嗮成個網頁平均要用 230 毫秒,理解得到嗮望到嘅係啲乜就平均要用 300 毫秒,做決策(「買唔買」同埋「要買邊樣嘢」)就平均要用咁多咁多毫秒,而腦部傳訊號落手嘅肌肉令手做出「撳掣」嘅動作就平均要用咁多咁多毫秒... 等等;將呢啲數值加埋之後,班設計者就可以估計到用家平均會喺個網頁上嘥大約幾耐嘅時間,而呢個數值可以攞嚟做易用度嘅指標之一-易用嘅電腦嘢係應該能夠俾用家快速達成目的嘅[5][6]。
評估
[編輯]喺實際應用上,人機互動專家會用各種方法評估一個系統嘅易用度,而呢啲評估方法有得分做兩大種[7][8]:
- 易用度測試(usability testing):指真係搵用家(受試者)返嚟試吓用個系統;喺呢個測試過程當中,設計者會要求啲受試者自由噉用吓,跟住又會叫佢哋試吓用某啲特定嘅功能嚟達到某啲里程碑;喺呢個測試過程當中,設計者會用觀察受試者嘅行為,又會某啲方法量度一啲反映易用度嘅指標,「指標」包括「受試者用咗幾多時間嚟達到里程碑」以及「有幾多百分比嘅受試者成功達到里程碑」呀噉-如果個系統易用,應該會出現「多數受試者都能夠喺短時間之內搞掂」嘅情況;而且設計者喺觀察受試者嘅行為嘅過程裏面,仲能夠得到「用家犯錯嗰陣傾向犯乜嘢錯」嘅資訊,而呢樣資訊都幫到設計者度吓個系統嘅設計要點樣執[9]。可以睇埋心理實驗。
- 易用度檢測(usability inspection):指靠易用度專家用客觀方法親自做評估;例如認知走查法(cognitive walkthrough)係一種成日用嘅易用度檢測做法,當一個設計者用認知走查法嗰陣,佢首先要列出嗮「如果用家想要用隻軟件達到某樣效果,需要經過邊啲步驟?」,例如評估緊隻繪圖軟件,列出如果用家想要增加幅圖嘅光度需要先後撳邊個掣;然後 foreach 步驟,設計者都會問幾條問題:
- 用家能唔能夠輕易睇得出要撳邊個掣?
- 用家能唔能夠理解隻軟件對嗰個功能嘅描述?
- ... 等等。個設計者會一路做以上嘅嘢,做到評估嗮隻軟件嘅各種功能為止[10][11]。
睇埋
[編輯]文獻
[編輯]- Mazumder, F. K., & Das, U. K. (2014). Usability guidelines for usable user interface (PDF). International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology, 3(9), 79-82.
攷
[編輯]- ↑ T. I. S. Organisation, "Ergonomic Requirements for Office Work with Visual Display Terminals, ISO 9241-11", (1998).
- ↑ Fioretti, G. (2007). The organizational learning curve. European Journal of Operational Research, 177(3), 1375-1384.
- ↑ De Laveaga, A., Wadman, M. C., Wirth, L., & Hallbeck, M. S. (2012). Ergonomics of novices and experts during simulated endotracheal intubation. Work, 41(Supplement 1), 4692-4698.
- ↑ Kainda, R., Flechais, I., & Roscoe, A. W. (2010, February). Security and usability: Analysis and evaluation (PDF). In 2010 International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security (pp. 275-282). IEEE.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Card, S.K; Moran, T. P; and Newell, A. The Model Human Processor: An Engineering Model of Human Performance. In K. R. Boff, L. Kaufman, & J. P. Thomas (Eds.), Handbook of Perception and Human Performance. Vol. 2: Cognitive Processes and Performance, 1986, pages 1-35.
- ↑ Liu, Yili; Feyen, Robert; and Tsimhoni, Omer. Queueing Network-Model Human Processor(QN-MHP): A Computational Architecture for Multitask Performance in Human-Machine Systems. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction. Volume 13, Number 1, March 2006, pages 37-70.
- ↑ Lewis, J. R. (2006). Usability testing. Handbook of human factors and ergonomics, 12, e30.
- ↑ Bastien, J. C. (2010). Usability testing: a review of some methodological and technical aspects of the method (PDF). International journal of medical informatics, 79(4), e18-e23.
- ↑ Dumas, J. S., Dumas, J. S., & Redish, J. (1999). A practical guide to usability testing. Intellect books.
- ↑ Blackmon, M. H., Polson, P. G., Kitajima, M., & Lewis, C. (2002, April). Cognitive walkthrough for the web (PDF). In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on human factors in computing systems (pp. 463-470).
- ↑ Spencer, R. (2000, April). The streamlined cognitive walkthrough method, working around social constraints encountered in a software development company (PDF). In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 353-359).
| 基本概念 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 用家介面 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 相關領域 | |||||||||||||||
| 拉雜概念 |
| ||||||||||||||
| 基本概念 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 軟件質素 |
| ||||
| 軟件開發 | |||||
| 開發模型 | |||||
| 相關領域 | |||||
| 重要概念 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 電腦理論 | |||||||||||
| 電腦系統 | |||||||||||
| 電腦通訊 | |||||||||||
| 程式編寫 | |||||||||||
| 電腦應用 |
| ||||||||||
| AI | |||||||||||
| 相關領域 | |||||||||||
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.









