Gini-coëfficiënt

| ■ ≤ 30 ■ 30-34.9 ■ 35-39.9 ■ 40-44.9 | ■ 45-49.9 ■ 50-54.9 ■ 55-59.9 ■ 60-64.9 ■ Geen gegevens |
De gini-coëfficiënt, ook wel gini-index, is een statistische maatstaf van de ongelijkheid in een verdeling. De gini-coëfficiënt wordt met name gebruikt in de economie om de ongelijkheid in inkomen of vermogen aan te geven, maar is geschikt om elke vorm van ongelijkmatige verspreiding te meten.
De gini-coëfficiënt is doorgaans een getal tussen nul en één en wordt soms uitgedrukt als percentage. De waarde nul correspondeert hierbij met volkomen gelijkheid (in het voorbeeld van de inkomensverdeling heeft iedereen hetzelfde inkomen) en één correspondeert met volkomen ongelijkheid (één persoon heeft al het inkomen en de rest heeft geen inkomen). Indien negatieve inkomens of vermogens (schulden) worden meegerekend, dan kan de gini-coëfficiënt een waarde groter dan één aannemen.
De gini-coëfficiënt werd ontwikkeld door de Italiaanse statisticus Corrado Gini en in 1912 gepubliceerd in zijn artikel Variabilità e mutabilità.[1]
Berekening
[bewerken | brontekst bewerken]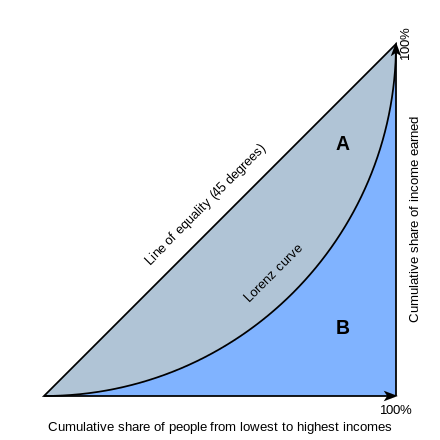
De gini-coëfficiënt is de verhouding van twee gebieden in de grafiek van de lorenz-curve. Deze tekent de proportie van het totale inkomen van een populatie (-as) ten opzichte van de cumulatieve inkomsten van de onderste van de bevolking.
Als het gebied is tussen de diagonale lijn en de lorenz-curve, en het gebied onder de lorenz-curve, dan is de gini-coëfficiënt gelijk aan . De gini-coëfficiënt wordt vaak benaderd met de meer praktische formule van Brown die er als volgt uitziet:
Hierin is:
- de gini-coëfficiënt
- de cumulatieve proportie van de variabele populatie (aandeel in de totale populatie)
- de cumulatieve proportie van het variabele inkomen (aandeel in het totale inkomen)
Zie ook
[bewerken | brontekst bewerken]- ↑ Gini, C. (1912) (Variabilità e mutabilità), C. Cuppini, Bologna, 156 pagina's. Herdrukt in Memorie di metodologica statistica (Ed. Pizetti E, Salvemini, T). Rome: Libreria Eredi Virgilio Veschi (1955)
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.










