Nota numeri
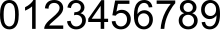
Nota numeri[1] est una ex pluribus notis ad numeros scribendos adhibitis. In mathematica nostri temporis plerumque numeri Arabici adhibentur, pro quibus vocabulum cifra saepe usurpatur (sed hoc etiam numerus nullus, zero, significare potest, de quo vide infra).
Ex aevo praehistorico homines variis notis usi sunt, lineis simplicibus incipientes, e.g. IIIII est quinque. Graeci antiqui litteras ex alphabeto secundum systema definitum adhibuerunt, e.g. ΣΜΑ est ducenti quadraginta unus. Romani quoque litteris usi sunt, sed secundum alium systema, e.g. LXIV est sexaginta quattuor.
Haec autem systemata ad numeros magnos scribendos parum sunt idonea. Medio aevo numeri Arabici (vel Indici) variis in formis late accepti sunt. Hi numeri utuntur notatione positionali, in qua cifrae, variis in locis positae, varias habent magnitudines; e.g. in notatione decimali, in qua basis est decem, 312 est (3 × 102) + (1 × 101) + (2 × 100); sive ter centi, semel decem, bis duo; sive trecenti duodecim.
De vocabulis
[recensere | fontem recensere]Locutio nota numeri reperitur apud Diomedem Grammaticum: "C nota praenominis, cum sola Gaium notat; item numeri cum centum significat".[2]
Vocabula cifra (seu cifera, ciphra, etc.) et zero deducuntur ab Arabico صفر ṣifr, quod notam nulli numeri ٠ (0 nostrum) significat. Ipsum nomen Arabicum est conversio Sancritici शून्य śūnya, "vacuus".[3]
Itaque in media Latinitate duas significationes habet, sicut scribit Carolus du Cange:
- CIFRAE, Chilerae, seu Ziferae, Notae numerales. Nostris Cifres, nunc Chiffres dicuntur hae notae arithmeticae 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 0. quarum prima est unitatis, secunda binarii, etc. 9. novenarii : 0. vero circularis nota, quam ex his solam alii vocant Ziferam, Georgius Valla Ziphram, per se quidem nihil significat ; sed aliis notis addita, numerum multiplicat.[4]
Nexus interni
Notae
[recensere | fontem recensere]Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
