ಪೀನಿಯಲ್ ಗ್ರಂಥಿ
| Pineal gland | |
|---|---|
| |
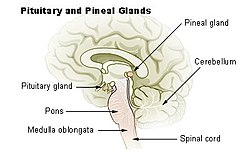
| Diagram of pituitary and pineal glands in the human brain | |
| ಲ್ಯಾಟಿನ್ | glandula pinealis |
| Gray's | subject #276 1277 |
| Artery | superior cerebellar artery |
| Precursor | Neural Ectoderm, Roof of Diencephalon |
| MeSH | Pineal+gland |
ಗ್ಲ್ಯಾಂಡುಲಾ ಪಿನಾಲಿಸ್ಮೆಶ್
| ಪೀನಲ್ ಗ್ರಂಥಿ | |
|---|---|
| center|250x250px | |
| ಮಾನವನ ಮೆದುಳಿನಲ್ಲಿರುವ ಪಿಟ್ಯುಟರಿ ಮತ್ತು ಪೀನಲ್ ಗ್ರಂಥಿಗಳ ರೇಖಾಚಿತ್ರ | |
| ಲ್ಯಾಟಿನ್ | |
| ಬೂದು ದೇಹ | ವಿಷಯ # 276 1277 Archived 2007-05-18 ವೇಬ್ಯಾಕ್ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ನಲ್ಲಿ. |
| class="external text" href="https://education.yahoo.com/reference/gray/subjects/subject?id=276#p1277 Archived 2007-05-18 ವೇಬ್ಯಾಕ್ ಮೆಷಿನ್ ನಲ್ಲಿ." rel="mw:ExtLink" | ಅಪಧಮನಿಗಳು | ಉನ್ನತ ಸೆರೆಬೆಲ್ಲಾರ್ ಅಪಧಮನಿ |
| ಮುನ್ಸೂಚನೆ | ನರ ಎಕ್ಟೋಡರ್ಮ್, ಡೈನ್ಸ್ಫಾಲನ್ನ ಮೇಲ್ oft ಾವಣಿ |
| (({ಮೆಶ್ನೇಮ್ಹಿಂಡಿ))} | |
ಪೀನಿಯಲ್ ಗ್ರಂಥಿ (ಪೀನಿಯಲ್ ಗಂಟು, ಎಪಿಫೈಸಿಸ್ ಸೆರೆಬ್ರಿ, ಎಪಿಫೈಸಿಸ್, ಅಥವಾ "ಮೂರನೇ ಕಣ್ಣು" ಎಂದೂ ಕರೆಯುತ್ತಾರೆ) ಕಶೇರುಕ ಪ್ರಾಣಿಗಳ ಮೆದುಳಿನಲ್ಲಿರುವ ಒಂದು ಸಣ್ಣ ಅಂತಃಸ್ರಾವಕ ಗ್ರಂಥಿಯಾಗಿದೆ. ಇದು ಸಿರೊಟೋನಿನ್ ಉತ್ಪನ್ನ ಮೆಲಟೋನಿನ್ ಅನ್ನು ಉತ್ಪಾದಿಸುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದು ಎಚ್ಚರಗೊಳ್ಳುವ / ಮಲಗುವ ಮಾದರಿಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕಾಲೋಚಿತ ಚಟುವಟಿಕೆಗಳನ್ನು ನಿಯಂತ್ರಿಸುವ ಹಾರ್ಮೋನ್ .[೧][೨] ಇದರ ಆಕಾರವು ಸಣ್ಣ ಪೈನ್ ಕೋನ್ ಅನ್ನು ಹೋಲುತ್ತದೆ (ಆದ್ದರಿಂದ ಅದಕ್ಕೆ ತಕ್ಕಂತೆ ಹೆಸರು) ಮತ್ತು ಇದು ಮೆದುಳಿನ ಮಧ್ಯಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿರುವ ಎರಡು ಅರ್ಧಗೋಳಗಳ ನಡುವಿನ ತೋಪಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಸೀಮಿತವಾಗಿದೆ, ಅಲ್ಲಿ ಎರಡು ವೃತ್ತಾಕಾರದ ಕಂಜೋಯಿನ್ಗಳು ಸೇರಿಕೊಳ್ಳುತ್ತವೆ.
ರಚನೆ ಮತ್ತು ಸಂಯೋಜನೆ
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]
ಮಾನವರಲ್ಲಿ, ಪೀನಲ್ ಗಂಟುಗಳು ಸಂಯೋಜಕ ಅಂಗಾಂಶದಲ್ಲಿನ ಅಂತರಗಳಿಂದ ಸುತ್ತುವರೆದಿರುವ ಪೀನಿಯಲ್ ಕೋಶಗಳ ವಿಭಜಿತ ಸಿನಾಪ್ಗಳಿಂದ ಕೂಡಿದೆ. ಗ್ರಂಥಿಯ ಮೇಲ್ಮೈ ಮೃದು ಕ್ಯಾಪ್ಸುಲ್ನಿಂದ ಆವೃತವಾಗಿದೆ.
ಪೀನಿಯಲ್ ಗ್ರಂಥಿಯು ಮುಖ್ಯವಾಗಿ ಪೀನಿಯಲ್ ಕೋಶಗಳನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತದೆ, ಆದರೆ ಇತರ ನಾಲ್ಕು ಜೀವಕೋಶದ ಪ್ರಕಾರಗಳನ್ನು ಗುರುತಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಇದು ಏಕಕೋಶೀಯವಾಗಿರುವುದರಿಂದ (ಹೊರಗಿನ ಪದರ ಮತ್ತು ಬಿಳಿ ದ್ರವ್ಯಕ್ಕೆ ಸಂಬಂಧಿಸಿದಂತೆ) ಇದನ್ನು ಗೆಡ್ಡೆ ಎಂದು ತಪ್ಪಾಗಿ ಪರಿಗಣಿಸಬಹುದು.[೩]
ಉಲ್ಲೇಖಗಳು
[ಬದಲಾಯಿಸಿ]- ↑ Macchi M, Bruce J (2004). "Human pineal physiology and functional significance of melatonin". Front Neuroendocrinol. 25 (3–4): 177–95. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2004.08.001. PMID 15589268.
- ↑ Arendt J, Skene DJ (2005). "Melatonin as a chronobiotic". Sleep Med Rev. 9 (1): 25–39. doi:10.1016/j.smrv.2004.05.002. PMID 15649736.
Exogenous melatonin has acute sleepiness-inducing and temperature-lowering effects during 'biological daytime', and when suitably timed (it is most effective around dusk and dawn) it will shift the phase of the human circadian clock (sleep, endogenous melatonin, core body temperature, cortisol) to earlier (advance phase shift) or later (delay phase shift) times.
- ↑ Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Prayson RA (November 2006). "An algorithmic approach to the brain biopsy—part I". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 130 (11): 1630–8. PMID 17076524.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
