Sistem Satelit Quasi-Zenith

Sistem Satelit Quasi-Zenith atau Quasi-Zenith Satellite System ( QZSS ) adalah sistem transfer waktu regional tiga satelit dalam pengembangan dan sistem augmentasi berbasis satelit untuk Global Positioning System yang akan menjadi penerima di Jepang. Satelit pertama "Michibiki" diluncurkan pada 11 September 2010.[1] Status operasional penuh diperkirakan pada 2013.[2][3] Pada bulan Maret 2013, Kantor Kabinet Jepang mengumumkan perluasan Sistem Satelit Kuasi-Zenit dari tiga satelit ke empat.[4] Kontrak senilai $ 526 juta dengan Mitsubishi Electric untuk pembangunan tiga satelit dijadwalkan diluncurkan sebelum akhir 2017. Sistem empat satelit dasar direncanakan akan beroperasi pada tahun 2018.[5]
Berita resmi oleh pemerintah Jepang pada tahun 2002, mengerjakan sebuah konsep untuk Sistem Satelit Kuasi-Zenit (QZSS), atau Juntencho eisei shisutemu ( bahasa Jepang), mulai dikembangkan oleh tim Advanced Space Business Corporation (ASBC), termasuk Mitsubishi Electric, Hitachi, dan GNSS Technologies Inc. Namun, ASBC ambruk pada tahun 2007. Pekerjaan diambil alih oleh Satellite Positioning Research and Application Center. SPAC dimiliki oleh empat departemen pemerintah Jepang: Kementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Olahraga, Ilmu Pengetahuan dan Teknologi, Kementerian Dalam Negeri dan Komunikasi, Kementerian Ekonomi, Perdagangan dan Industri, dan Kementerian Tanah, Infrastruktur, Transportasi dan Pariwisata.[6]
QZSS ditargetkan untuk memberikan layanan posisi yang sangat tepat dan stabil di wilayah Asia-Oceania, sambil menjaga kompatibilitas dengan GPS.[7] Satelit ketiga diluncurkan ke orbit pada tanggal 19 Agustus 2017. Yang keempat diluncurkan pada tanggal 10 Oktober 2017.[8] The fourth was launched on October 10, 2017.[9]
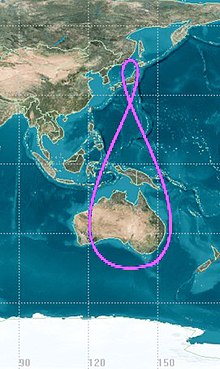
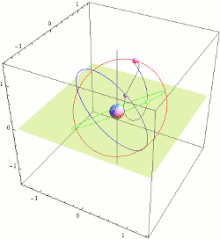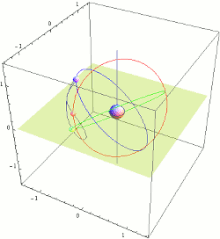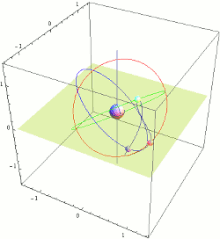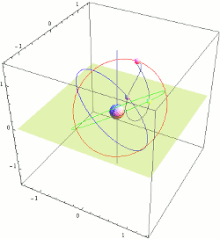
QZSS menggunakan tiga satelit, masing-masing 120 ° terpisah, dengan orbit yang sangat miring, sedikit elips, dan geosynchronous. Karena kecenderungan ini, mereka tidak geostasioner; Mereka tidak tinggal di tempat yang sama di langit. Sebagai gantinya, jejak tanah mereka adalah pola angka-8 asimetris (analemma), dirancang untuk memastikan bahwa muatannya hampir di atas kepala (ketinggian 60 ° atau lebih) di atas Jepang setiap saat.
Lihat pula
Referensi
- ^ "Launch Result of the First Quasi-Zenith Satellite 'MICHIBIKI' by H-IIA Launch Vehicle No. 18". 2010-09-11. Diakses tanggal 2011-12-12.
- ^ "QZSS in 2010". Magazine article. Asian Surveying and Mapping. 2009-05-07. Diakses tanggal 2009-05-07.[pranala nonaktif]
- ^ "GNSS All Over the World". The System. GPS World Online. 2007-11-01. Diarsipkan dari versi asli tanggal August 23, 2011. Diakses tanggal 2011-12-12.
- ^ http://www.spaceflightnow.com/news/n1304/04qzss/ Japan to build fleet of navigation satellites 2013-04-04 Retrieved 2013-04-05
- ^ "Service Overview - What is the QZSS?". Cabinet Office, Government of Japan. Diakses tanggal 2016-01-20.
- ^ "Service Status of QZSS" (PDF). 2008-12-12. Diarsipkan dari versi asli (PDF) tanggal July 25, 2011. Diakses tanggal 2009-05-07.
- ^ "[Movie] Quasi-Zenith Satellite System "QZSS"". Quasi-Zenith Satellite System(QZSS) (dalam bahasa Inggris). Diakses tanggal 19 July 2017.
- ^ https://spaceflightnow.com/2017/08/19/japan-launches-navigation-satellite-after-week-long-delay/
- ^ https://spaceflightnow.com/launch-schedule/
- Petrovski, Ivan G. QZSS - Japan's New Integrated Communication and Positioning Service for Mobile Users. GPS World Online. June 1, 2003.
- Kallender-Umezu, Paul. Japan Seeking 13 Percent Budget Hike for Space Activities. Space.com. September 7, 2004.
- QZSS / MSAS Status Kogure, Satoshi. Presentation at the 47th Meeting of the Civil Global Positioning System Service Interface Committee (CGSIC). September 25, 2007.
- Government Of Japan QZSS site
- JAXA QZSS site Diarsipkan 2016-10-21 di Wayback Machine.(Jepang)
- JAXA MICHIBIKI data site (Jepang)
- JAXA MICHIBIKI data site, English subsite
- JAXA Quasi-Zenith Satellite-1 "MICHIBIKI" Diarsipkan 2013-01-22 di Wayback Machine.
- JAXA MICHIBIKI Special Site
- JAXA QZSS Twitter account (Jepang)
- ESA Navipedia QZSS article
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
