| Octane
|

|
 |
| Formule développée et représentation 3D du n-octane |
| Identification |
| Nom UICPA
|
octane
|
| Synonymes
|
n-octane
|
| No CAS
|
|
| No ECHA
|
100.003.539 |
| No CE
|
203-892-1
|
| No RTECS
|
RG8400000
|
| DrugBank
|
DB02440
|
| PubChem
|
356
|
| ChEBI
|
17590
|
| SMILES
|
|
| InChI
|
InChI : vue 3D InChI=1S/C8H18/c1-3-5-7-8-6-4-2/h3-8H2,1-2H3 InChIKey : TVMXDCGIABBOFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Apparence
|
liquide incolore, d'odeur caractéristique
|
| Propriétés chimiques |
| Formule
|
C8H18 [Isomères]
|
| Masse molaire[2]
|
114,228 5 ± 0,007 7 g/mol
C 84,12 %, H 15,88 %,
|
| Diamètre moléculaire
|
0,655 nm[1]
|
| Propriétés physiques |
| T° fusion
|
−56,8 °C[3]
|
| T° ébullition
|
125,67 °C[4]
|
| Solubilité
|
dans l'eau : insoluble[3]
|
| Paramètre de solubilité δ
|
15,6 MPa1/2 (25 °C)[5]
|
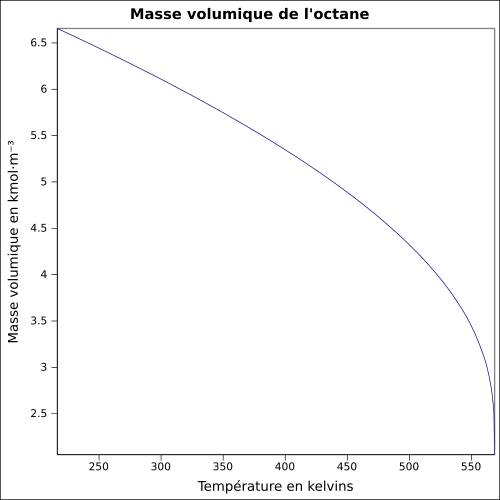
| Masse volumique
|
0,70 g·cm-3[3]
équation[6] : 
Masse volumique du liquide en kmol·m-3 et température en kelvins, de 216,38 à 568,7 K.
Valeurs calculées :
0,6992 g·cm-3 à 25 °C.
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
ρ (kmol·m-3) |
ρ (g·cm-3) |
|---|
| 216,38 |
−56,77 |
6,6558 |
0,7603 |
| 239,87 |
−33,28 |
6,50778 |
0,74339 |
| 251,61 |
−21,54 |
6,43221 |
0,73476 |
| 263,36 |
−9,79 |
6,35551 |
0,726 |
| 275,1 |
1,95 |
6,27761 |
0,7171 |
| 286,84 |
13,69 |
6,19843 |
0,70805 |
| 298,59 |
25,44 |
6,11788 |
0,69885 |
| 310,33 |
37,18 |
6,03587 |
0,68948 |
| 322,08 |
48,93 |
5,95229 |
0,67994 |
| 333,82 |
60,67 |
5,86701 |
0,67019 |
| 345,56 |
72,41 |
5,77989 |
0,66024 |
| 357,31 |
84,16 |
5,69078 |
0,65006 |
| 369,05 |
95,9 |
5,59949 |
0,63963 |
| 380,8 |
107,65 |
5,5058 |
0,62893 |
| 392,54 |
119,39 |
5,40948 |
0,61793 |
|
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
ρ (kmol·m-3) |
ρ (g·cm-3) |
|---|
| 404,28 |
131,13 |
5,31024 |
0,60659 |
| 416,03 |
142,88 |
5,20772 |
0,59488 |
| 427,77 |
154,62 |
5,1015 |
0,58275 |
| 439,52 |
166,37 |
4,99108 |
0,57014 |
| 451,26 |
178,11 |
4,87582 |
0,55697 |
| 463 |
189,85 |
4,75491 |
0,54316 |
| 474,75 |
201,6 |
4,62728 |
0,52858 |
| 486,49 |
213,34 |
4,49151 |
0,51307 |
| 498,24 |
225,09 |
4,34563 |
0,49641 |
| 509,98 |
236,83 |
4,18671 |
0,47825 |
| 521,72 |
248,57 |
4,01017 |
0,45809 |
| 533,47 |
260,32 |
3,80808 |
0,435 |
| 545,21 |
272,06 |
3,56433 |
0,40716 |
| 556,96 |
283,81 |
3,23469 |
0,3695 |
| 568,7 |
295,55 |
2,058 |
0,23509 |
|
|
| T° d'auto-inflammation
|
220 °C[3]
|
| Point d’éclair
|
13 °C (coupelle fermée)[3]
|
| Limites d’explosivité dans l’air
|
1,0–6,5 %vol[3]
|
| Pression de vapeur saturante
|
à 20 °C : 1,33 kPa[3]
équation[6] : 
Pression en pascals et température en kelvins, de 216,38 à 568,7 K.
Valeurs calculées :
1 870,98 Pa à 25 °C.
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
P (Pa) |
|---|
| 216,38 |
−56,77 |
2,1083 |
| 239,87 |
−33,28 |
26,16 |
| 251,61 |
−21,54 |
74,95 |
| 263,36 |
−9,79 |
192,2 |
| 275,1 |
1,95 |
447,87 |
| 286,84 |
13,69 |
960,72 |
| 298,59 |
25,44 |
1 917,56 |
| 310,33 |
37,18 |
3 593,78 |
| 322,08 |
48,93 |
6 373,11 |
| 333,82 |
60,67 |
10 764,73 |
| 345,56 |
72,41 |
17 416,47 |
| 357,31 |
84,16 |
27 123 |
| 369,05 |
95,9 |
40 829,23 |
| 380,8 |
107,65 |
59 629,11 |
| 392,54 |
119,39 |
84 761,13 |
|
| T (K) |
T (°C) |
P (Pa) |
|---|
| 404,28 |
131,13 |
117 601,63 |
| 416,03 |
142,88 |
159 657,51 |
| 427,77 |
154,62 |
212 559,62 |
| 439,52 |
166,37 |
278 058,17 |
| 451,26 |
178,11 |
358 021,13 |
| 463 |
189,85 |
454 436,52 |
| 474,75 |
201,6 |
569 419,04 |
| 486,49 |
213,34 |
705 221,59 |
| 498,24 |
225,09 |
864 251,95 |
| 509,98 |
236,83 |
1 049 094,63 |
| 521,72 |
248,57 |
1 262 538,39 |
| 533,47 |
260,32 |
1 507 609,24 |
| 545,21 |
272,06 |
1 787 609,5 |
| 556,96 |
283,81 |
2 106 163 |
| 568,7 |
295,55 |
2 467 300
|
|
 |
| Viscosité dynamique
|
0,515 mPa·s à 24,95 °C[7]
|
| Point critique
|
2 490 kPa[8], 295,68 °C[4]
|
| Vitesse du son
|
1 197 m·s-1 à 20 °C[9]
|
| Thermochimie |
| ΔfH0liquide
|
−250,31 kJ·mol-1[10]
|
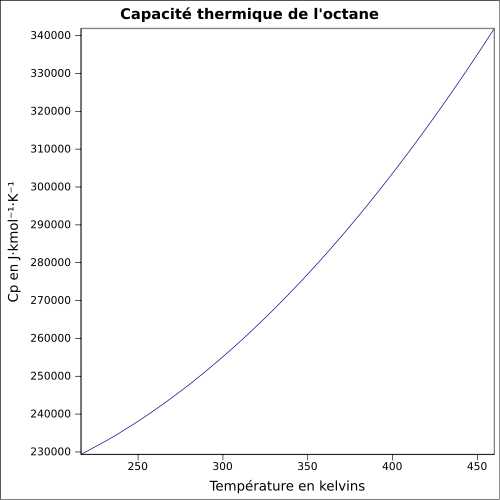
| Cp
|
équation[6] : 
Capacité thermique du liquide en J·kmol-1·K-1 et température en kelvins, de 216,38 à 460 K.
Valeurs calculées :
254,427 J·mol-1·K-1 à 25 °C.
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 216,38 |
−56,77 |
229 340 |
2 008 |
| 232 |
−41,15 |
233 144 |
2 041 |
| 240 |
−33,15 |
235 272 |
2 060 |
| 248 |
−25,15 |
237 523 |
2 079 |
| 256 |
−17,15 |
239 896 |
2 100 |
| 265 |
−8,15 |
242 713 |
2 125 |
| 273 |
−0,15 |
245 347 |
2 148 |
| 281 |
7,85 |
248 103 |
2 172 |
| 289 |
15,85 |
250 983 |
2 197 |
| 297 |
23,85 |
253 985 |
2 223 |
| 305 |
31,85 |
257 110 |
2 251 |
| 313 |
39,85 |
260 358 |
2 279 |
| 321 |
47,85 |
263 729 |
2 309 |
| 330 |
56,85 |
267 667 |
2 343 |
| 338 |
64,85 |
271 299 |
2 375 |
|
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 346 |
72,85 |
275 053 |
2 408 |
| 354 |
80,85 |
278 930 |
2 442 |
| 362 |
88,85 |
282 929 |
2 477 |
| 370 |
96,85 |
287 052 |
2 513 |
| 378 |
104,85 |
291 297 |
2 550 |
| 386 |
112,85 |
295 665 |
2 588 |
| 395 |
121,85 |
300 725 |
2 633 |
| 403 |
129,85 |
305 354 |
2 673 |
| 411 |
137,85 |
310 105 |
2 715 |
| 419 |
145,85 |
314 979 |
2 757 |
| 427 |
153,85 |
319 976 |
2 801 |
| 435 |
161,85 |
325 096 |
2 846 |
| 443 |
169,85 |
330 338 |
2 892 |
| 451 |
177,85 |
335 703 |
2 939 |
| 460 |
186,85 |
341 890 |
2 993 |
|
équation[11] : 
Capacité thermique du gaz en J·mol-1·K-1 et température en kelvins, de 200 à 1 500 K.
Valeurs calculées :
192,376 J·mol-1·K-1 à 25 °C.
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 200 |
−73,15 |
141 360 |
1 237 |
| 286 |
12,85 |
186 248 |
1 630 |
| 330 |
56,85 |
208 171 |
1 822 |
| 373 |
99,85 |
228 847 |
2 003 |
| 416 |
142,85 |
248 739 |
2 178 |
| 460 |
186,85 |
268 247 |
2 348 |
| 503 |
229,85 |
286 453 |
2 508 |
| 546 |
272,85 |
303 787 |
2 659 |
| 590 |
316,85 |
320 606 |
2 807 |
| 633 |
359,85 |
336 133 |
2 943 |
| 676 |
402,85 |
350 759 |
3 071 |
| 720 |
446,85 |
364 793 |
3 193 |
| 763 |
489,85 |
377 606 |
3 306 |
| 806 |
532,85 |
389 544 |
3 410 |
| 850 |
576,85 |
400 876 |
3 509 |
|
T
(K) |
T
(°C) |
Cp
 |
Cp
 |
|---|
| 893 |
619,85 |
411 114 |
3 599 |
| 936 |
662,85 |
420 561 |
3 682 |
| 980 |
706,85 |
429 450 |
3 759 |
| 1 023 |
749,85 |
437 425 |
3 829 |
| 1 066 |
792,85 |
444 750 |
3 893 |
| 1 110 |
836,85 |
451 635 |
3 954 |
| 1 153 |
879,85 |
457 833 |
4 008 |
| 1 196 |
922,85 |
463 580 |
4 058 |
| 1 240 |
966,85 |
469 075 |
4 106 |
| 1 283 |
1 009,85 |
474 155 |
4 151 |
| 1 326 |
1 052,85 |
479 041 |
4 194 |
| 1 370 |
1 096,85 |
483 940 |
4 237 |
| 1 413 |
1 139,85 |
488 736 |
4 278 |
| 1 456 |
1 182,85 |
493 651 |
4 322 |
| 1 500 |
1 226,85 |
498 925 |
4 368 |
|
|
| PCS
|
47,9 MJ·kg-1[12]
|
| Propriétés optiques |
| Indice de réfraction
|
 1,3951[1] 1,3951[1]
|
| Précautions |
| SGH |
H224, H304, H315, H335, H410, P201, P235, P301, P310, P331, P370, P378 et P403H224 : Liquide et vapeurs extrêmement inflammables
H304 : Peut être mortel en cas d'ingestion et de pénétration dans les voies respiratoires
H315 : Provoque une irritation cutanée
H335 : Peut irriter les voies respiratoires
H410 : Très toxique pour les organismes aquatiques, entraîne des effets à long terme
P201 : Se procurer les instructions avant utilisation.
P235 : Tenir au frais.
P301 : En cas d'ingestion :
P310 : Appeler immédiatement un CENTRE ANTIPOISON ou un médecin.
P331 : NE PAS faire vomir.
P370 : En cas d’incendie :
P378 : Utiliser … pour l’extinction.
P403 : Stocker dans un endroit bien ventilé.
|
| SIMDUT[13] |
 
B2, D2B, B2 : Liquide inflammable point d'éclair = 13,33 °C, coupelle fermée, méthode Tag D2B : Matière toxique ayant d'autres effets toxiques irritation de la peau Divulgation à 1,0 % selon la liste de divulgation des ingrédients |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| Directive 67/548/EEC |
Numéro index : 601-009-00-8Classification : F; R11 - Xn; R65 - Xi; R38 - R67 - N; R50-53 Symboles : Xn : NocifF : Facilement inflammableN : Dangereux pour l’environnementPhrases R : R11 : Facilement inflammable. R38 : Irritant pour la peau. R65 : Nocif : peut provoquer une atteinte des poumons en cas d’ingestion. R67 : L’inhalation de vapeurs peut provoquer somnolence et vertiges. R50/53 : Très toxique pour les organismes aquatiques, peut entraîner des effets néfastes à long terme pour l’environnement aquatique. Phrases S : (S2) : Conserver hors de portée des enfants. S9 : Conserver le récipient dans un endroit bien ventilé. S16 : Conserver à l’écart de toute flamme ou source d’étincelles - Ne pas fumer. S29 : Ne pas jeter les résidus à l’égout. S33 : Éviter l’accumulation de charges électrostatiques. S60 : Éliminer le produit et son récipient comme un déchet dangereux. S61 : Éviter le rejet dans l’environnement. Consulter les instructions spéciales/la fiche de données de sécurité. S62 : En cas d’ingestion, ne pas faire vomir. Consulter immédiatement un médecin et lui montrer l’emballage ou l’étiquette.
|
| Transport |
Code Kemler :33 : matière liquide très inflammable (point d'éclair inférieur à 23 °C) Numéro ONU :1262 : OCTANES Classe :3 Étiquette : 3 3 : Liquides inflammables Emballage :Groupe d'emballage II : matières moyennement dangereuses ; |
| Écotoxicologie |
| LogP
|
4,00-5,18[3]
|
| Seuil de l’odorat
|
bas : 15 ppm
haut : 235 ppm[14]
|
|
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. |
modifier  |