Gamma Leporis
| Ascension droite | 05h 44m 27,8s |
|---|---|
| Déclinaison | −22° 26′ 54″ |
| Constellation | Lièvre |
| Magnitude apparente | 3,59 |
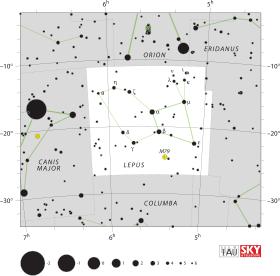
Localisation dans la constellation : Lièvre | |
| Type spectral | F6 V |
|---|---|
| Indice U-B | −0,01 |
| Indice B-V | 0,47 |
| Variabilité | Aucune |
| Vitesse radiale | −9,7 km/s |
|---|---|
| Mouvement propre |
μα = −292,42 mas/a μδ = −368,45 mas/a |
| Parallaxe | 111,69 ± 0,60 mas |
| Distance |
29,2 ± 0,2 al (8,85 ± 0,05 pc) |
| Magnitude absolue | 3,83/6,42 |
| Masse | 1,2 M☉ |
|---|---|
| Rayon | 1,3 R☉ |
| Luminosité | 2,6 L☉ |
| Température | 6 439 K |
| Métallicité | 82 % |
| Rotation | 11 km/s |
| Âge | ? a |
Désignations
Gamma Leporis (γ Lep / γ Leporis) est une étoile située à environ 29 années-lumière de la Terre. Il s'agit d'une naine jaune-blanc de type spectral F6V. Elle forme une étoile binaire avec l'étoile de sixième magnitude AK Leporis, avec qui elle partage un mouvement propre commun. Localisée à 96 secondes d'arc, AK Leporis est une naine orange de type spectral K2V[2].
Gamma Leporis se trouve dans la partie centrale sud de la constellation du Lièvre, au sud-est de Beta Leporis et au sud-ouest de Delta Leporis. Le système fait partie du Courant d'étoiles de la Grande Ourse.
Recherche de planètes
[modifier | modifier le code]À cause de ses caractéristiques stellaires et de sa distance à la Terre, Gamma Leporis était considérée comme une cible prioritaire pour la mission de la NASA Terrestrial Planet Finder (annulée en 2011). Elle était classée huitième dans l'ordre d'importance parmi 100 étoiles comprises dans ce projet, lequel avait pour objectif de détecter et d'étudier des planètes telluriques.
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- (en) * gam Lep -- High proper-motion Star sur la base de données Simbad du Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- (en) P. P. Eggleton et A. A. Tokovinin, « A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems », Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, vol. 389, no 2, , p. 869–879 (DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, Bibcode 2008MNRAS.389..869E, arXiv 0806.2878, lire en ligne)
Liens externes
[modifier | modifier le code]- (en) Gamma Leporis sur la base de données Simbad du Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- (en) Overview on Gamma Leporis (Solstation)
- (en) NASA NStars Database
- (en) Stellar Database
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.