نویز فاز
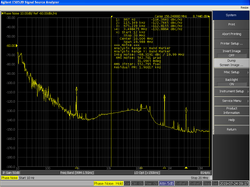

در پردازش سیگنال، نویز فاز، بازنمایش حوزه فرکانس اُفتوخیز تصادفی در فاز یک شکل موج است که متناظر با انحرافات حوزه زمان از تناوبمندی کامل («لغزش») است. بهطور کلی، مهندسان فرکانس-رادیویی از نویز فاز یک نوسانساز صحبت میکنند، در حالی که مهندسان سیستم دیجیتال با لغزش ساعت کار میکنند.
تعاریف
[ویرایش]از لحاظ تاریخی دو تعریف متناقض و در عین حال پرکاربرد برای نویز فاز وجود داشتهاست. برخی از نویسندگان، نویز فاز را تنها چگالی طیفی فاز سیگنال تعریف میکنند،[۱] در حالی که تعریف دیگر به طیف فاز (که با طیف دامنه جفت میشود) اشاره دارد که از تخمین طیفی خود سیگنال حاصل میشود.[۲] هر دو تعریف در فرکانسهای آفست که به خوبی از حامل حذف شدهاند، نتیجه یکسانی دارند. با این حال، در آفستهای نزدیک، این دو تعریف متفاوت هستند.[۳]
IEEE نویز فاز را به صورت ℒ(f) = Sφ(f)/2 تعریف میکند که در آن «ناپایداری فاز» Sφ(f) چگالی طیفی یکطرفه انحراف فاز سیگنال است.[۴] اگرچه Sφ(f) یک تابع یکطرفه است، اما «چگالی طیفی دوباندجانبی اُفتوخیز فاز» را نشان میدهد.[۵][نیازمند شفافسازی] نماد ℒ یک دستنویس پیوسته (به انگلیسی: script) (حرف بزرگ یا بزرگ) L نامیده میشود.[۶]
جستارهای وابسته
[ویرایش]- واریانس آلن
- نویز فلیکر
- معادله لیسون
- بیشینه خطای بازه زمانی
- چگالی طیفی نویز
- چگالی طیفی
- فاز طیفی
- نوسانساز نوری-الکترونیکی
منابع
[ویرایش]- ↑ Rutman, J.; Walls, F. L. (June 1991), "Characterization of frequency stability in precision frequency sources" (PDF), Proceedings of the IEEE, 79 (6): 952–960, Bibcode:1991IEEEP..79..952R, doi:10.1109/5.84972
- ↑ Demir, A.; Mehrotra, A.; Roychowdhury, J. (May 2000), "Phase noise in oscillators: a unifying theory and numerical methods for characterization" (PDF), IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 47 (5): 655–674, doi:10.1109/81.847872, ISSN 1057-7122, archived from the original (PDF) on 31 March 2011, retrieved 5 March 2022
- ↑ Navid, R.; Jungemann, C.; Lee, T. H.; Dutton, R. W. (2004), "Close-in phase noise in electrical oscillators", Proc. SPIE Symp. Fluctuations and Noise, Maspalomas, Spain
- ↑ Vig, John R.; Ferre-Pikal, Eva. S.; Camparo, J. C.; Cutler, L. S.; Maleki, L.; Riley, W. J.; Stein, S. R.; Thomas, C.; Walls, F. L. (26 March 1999), IEEE Standard Definitions of Physical Quantities for Fundamental Frequency and Time Metrology – Random Instabilities, IEEE, ISBN 978-0-7381-1754-6, IEEE Std 1139-1999, see definition 2.7.
- ↑ (IEEE 1999), stating ℒ(f) "is one half of the double-sideband spectral density of phase fluctuations."
- ↑ (IEEE 1999)
مطالعه بیشتر
[ویرایش]- Rubiola, Enrico (2008), Phase Noise and Frequency Stability in Oscillators, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-88677-2
- Wolaver, Dan H. (1991), Phase-Locked Loop Circuit Design, Prentice Hall, ISBN 978-0-13-662743-2
- Lax, M. (August 1967), "Classical noise. V. Noise in self-sustained oscillators", Physical Review, 160 (2): 290–307, Bibcode:1967PhRv..160..290L, doi:10.1103/PhysRev.160.290
- Hajimiri, A.; Lee, T. H. (February 1998), "A general theory of phase noise in electrical oscillators" (PDF), IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33 (2): 179–194, Bibcode:1998IJSSC..33..179H, doi:10.1109/4.658619, archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-03-05, retrieved 2021-09-16
- Pulikkoonattu, R. (June 12, 2007), Oscillator Phase Noise and Sampling Clock Jitter (PDF), Tech Note, Bangalore, India: ST Microelectronics, retrieved March 29, 2012
- Chorti, A.; Brookes, M. (September 2006), "A spectral model for RF oscillators with power-law phase noise" (PDF), IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 53 (9): 1989–1999, doi:10.1109/TCSI.2006.881182, hdl:10044/1/676, S2CID 8855005
- Rohde, Ulrich L.; Poddar, Ajay K.; Böck, Georg (May 2005), The Design of Modern Microwave Oscillators for Wireless Applications, New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 978-0-471-72342-4
- Ulrich L. Rohde, A New and Efficient Method of Designing Low Noise Microwave Oscillators, https://depositonce.tu-berlin.de/bitstream/11303/1306/1/Dokument_16.pdf
- Ajay Poddar, Ulrich Rohde, Anisha Apte, “ How Low Can They Go, Oscillator Phase noise model, Theoretical, Experimental Validation, and Phase Noise Measurements”, IEEE Microwave Magazine, Vol. 14, No. 6, pp. 50–72, September/October 2013.
- Ulrich Rohde, Ajay Poddar, Anisha Apte, “Getting Its Measure”, IEEE Microwave Magazine, Vol. 14, No. 6, pp. 73–86, September/October 2013
- U. L. Rohde, A. K. Poddar, Anisha Apte, “Phase noise measurement and its limitations”, Microwave Journal, pp. 22–46, مه ۲۰۱۳
- A. K. Poddar, U.L. Rohde, “Technique to Minimize Phase Noise of Crystal Oscillators”, Microwave Journal, pp. 132–150, May 2013.
- A. K. Poddar, U. L. Rohde, and E. Rubiola, “Phase noise measurement: Challenges and uncertainty”, 2014 IEEE IMaRC, Bangalore, Dec ۲۰۱۴.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
