ZZ Boötis
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Boötes |
| Right ascension | 13h 56m 09.5178s[2] |
| Declination | +25° 55′ 07.3547″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.79–7.44[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F2 IV-V + F2 IV-V[4] |
| B−V color index | +0.36[5] |
| Variable type | Algol[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | -29.50[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −97.004±0.057[2] mas/yr Dec.: −6.164±0.061[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 9.3114 ± 0.0381 mas[2] |
| Distance | 350 ± 1 ly (107.4 ± 0.4 pc) |
| Absolute bolometric magnitude (Mbol) | 2.17 / 2.30[4] |
| Orbit[4] | |
| Period (P) | 4.991744 d |
| Inclination (i) | 88.6 ± 0.1° |
| Semi-amplitude (K1) (primary) | 93.7 ± 2.1 km/s |
| Semi-amplitude (K2) (secondary) | 94.0 ± 2.1 km/s |
| Details | |
| ZZ Boo A | |
| Mass | 1.71 ± 0.06[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.28 ± 0.06[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 10.7[4] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.72 ± 0.10[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 6,860 ± 20[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.10 ± 0.08[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 11.9 ± 0.4[7] km/s |
| ZZ Boo B | |
| Mass | 1.70 ± 0.06[4] M☉ |
| Radius | 2.15 ± 0.06[4] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 9.95[4] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 3.84 ± 0.10[7] cgs |
| Temperature | 6930 ± 20[7] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.03 ± 0.10[7] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 19.3 ± 0.8[7] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
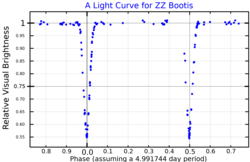
ZZ Boötis is a star system in the constellation Boötes. It varies from magnitude 6.79 to 7.44 over five days.[9] Based on its parallax, measured by the Gaia spacecraft, it is about 350 light-years (110 parsecs) away.[2]
Observational history
[edit]In 1950 Grigory Shajn determined that this star is a double-lined spectroscopic binary, with an approximate period of 4.96 days. Sergei Gaposchkin found from an examination of photographic plates, in 1951, that it was an Algol-type eclipsing binary system.[10] The primary and secondary eclipses are of equal depth, 0.65 magnitudes, meaning the brightness drops by nearly half.[3] The eclipses make up only 6% of the orbital period.[9]
ZZ Boötis is a binary star system, specifically an eclipsing binary.[9] The component stars appear to be of almost equal mass, differing by only 3%.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ McNamara, D. H.; Hansen, H. K.; Wilcken, S. K. (April 1971). "Photometry of the Eclipsing Star ZZ Bootis". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 83 (492): 192. Bibcode:1971PASP...83..192M. doi:10.1086/129099. S2CID 119982496. Retrieved 7 November 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ^ a b c Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....102025S.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Cester, B.; Giuricin, G.; Mardirossian, F.; Mezzetti, M. (1978). "Revised spectrographic and photometric elements of ZZ Boo". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 32: 347–350. Bibcode:1978A&AS...32..347C.
- ^ a b Popper, D. M. (1983). "The F-type eclipsing binaries ZZ Bootis, CW Eridani, and BK Pegasi". Astronomical Journal. 88: 1242–56. Bibcode:1983AJ.....88.1242P. doi:10.1086/113415. ISSN 0004-6256.
- ^ Pourbaix, D.; Tokovinin, A. A.; Batten, A. H.; Fekel, F. C.; Hartkopf, W. I.; Levato, H.; Morrell, N. I.; Torres, G.; Udry, S. (2004). "SB9: The ninth catalogue of spectroscopic binary orbits". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 424 (2): 727–732. arXiv:astro-ph/0406573. Bibcode:2004A&A...424..727P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041213. S2CID 119387088.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Kang, Young-Woon; Yushchenko, Alexander; Hong, Kyengsoo; Kim, Sungeun; Yushchenko, Volodymyr (2012). "Chemical Composition of the Components of Eclipsing Binary Star ZZ Bootis". The Astronomical Journal. 144 (2): 35–45. Bibcode:2012AJ....144...35K. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/144/2/35.
- ^ "ZZ Boo". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg.
- ^ a b c Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "ZZ Boötis". AAVSO Website. American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 5 August 2014.
- ^ Gaposchkin, S. (1951). "The system of RZ Eridani and a new bright eclipsing variable with double-lined spectrum". The Astronomical Journal. 56: 125. Bibcode:1951AJ.....56..125G. doi:10.1086/106546.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.