Wolffenstein–Böters reaction
The Wolffenstein–Böters reaction is an organic reaction converting benzene to picric acid by a mixture of aqueous nitric acid and mercury(II) nitrate.[1][2][3]
The reaction, which involves simultaneous nitration and oxidation, was first reported by the German chemists Richard Wolffenstein and Oskar Böters in 1906.[4]
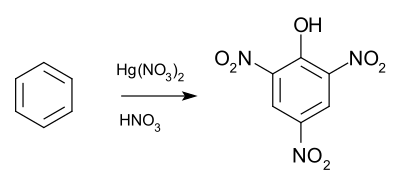
According to one series of studies the mercury nitrate first takes benzene to the corresponding nitroso compound and through the diazonium salt to the phenol. The presence of nitrite is essential for the reaction; picric acid formation is prevented when urea, a trap for nitrous acid, is added to the mixture. From then on the reaction proceeds as a regular aromatic nitration.[5][6]
A conceptually related reaction is the Bohn–Schmidt reaction, dating to 1889, which involves the hydroxylation of hydroxyanthraquinone with sulfuric acid and lead or selenium to a polyhydroxylated anthraquinone.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
