Pallidothalamic tracts
| Pallidothalamic tracts | |
|---|---|
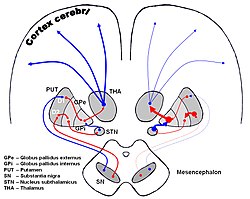 The image shows dopaminergic pathways of the human brain in normal condition (left) and Parkinsons Disease (right). Red Arrows indicate suppression of the target, blue arrows indicate stimulation of target structure. (Pallidothalamic connections visible but not labeled, as red line from GPi to THA.) | |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy |
The pallidothalamic tracts (or pallidothalamic connections)[1] are a part of the basal ganglia. They provide connectivity between the internal globus pallidus (GPi) and the thalamus, primarily the ventral anterior nucleus and the ventral lateral nucleus.
Anatomy
They are composed of the ansa lenticularis, the lenticular fasciculus (field H2 of Forel), and the thalamic fasciculus (field H1 of Forel).
- The ansa lenticularis is composed of fibers that pass from the ventral aspect of the globus pallidus and sweep around the posterior limb of the internal capsule. They connect with the fibers of the lenticular fasciculus in the field H of Forel to form the thalamic fasciculus.
- The lenticular fascicles is composed of fibers that pass from the internal part of the globus pallidus, through the posterior limb of the internal capsule, around the zona incerta. These fibers connect with the fibers of the ansa lenticularis in the field H of Forel to form the thalamic fasciculus.
- The thalamic fasciculus is formed by the fibers of the ansa lenticularis and the lenticular fasciculus that merge in the field H of Forel. The fibers of this fasciculus then travel to the thalamus and primarily terminate in the ventral anterior nucleus and ventral lateral nucleus.[2] Some fibers travel to the interthalamic nuclei.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
