Newton-metre
| Newton-metre | |
|---|---|
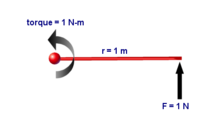 One newton-metre is the torque resulting from a force of one newton applied perpendicularly to the end of a moment arm that is one metre long. | |
| General information | |
| Unit system | SI |
| Unit of | torque |
| Symbol | N⋅m, N m |
| Conversions | |
| 1 N⋅m in ... | ... is equal to ... |
| FPS system | 0.73756215 lbf.ft |
| inch⋅pound-force | 8.8507 in lbf |
| inch⋅ounce-force | 141.6 in oz |
The newton-metre or newton-meter (also non-hyphenated, newton metre or newton meter; symbol N⋅m[1] or N m[1])[a] is the unit of torque (also called moment) in the International System of Units (SI). One newton-metre is equal to the torque resulting from a force of one newton applied perpendicularly to the end of a moment arm that is one metre long.
The unit is also used less commonly as a unit of work, or energy, in which case it is equivalent to the more common and standard SI unit of energy, the joule.[2] In this usage the metre term represents the distance travelled or displacement in the direction of the force, and not the perpendicular distance from a fulcrum as it does when used to express torque. This usage is generally discouraged,[3] since it can lead to confusion as to whether a given quantity expressed in newton-metres is a torque or a quantity of energy.[4] However, since torque represents energy transferred or expended per angle of revolution, one newton-metre of torque is equivalent to one joule per radian.[4]
Newton-metres and joules are dimensionally equivalent in the sense that they have the same expression in SI base units,
but are distinguished in terms of applicable kind of quantity, to avoid misunderstandings when a torque is mistaken for an energy or vice versa. Similar examples of dimensionally equivalent units include Pa versus J/m3, Bq versus Hz, and ohm versus ohm per square.
Conversion factors
[edit]- 1 kilogram-force metre = 9.80665 N⋅m[5][6]
- 1 newton-metre ≈ 0.73756215 pound-force-feet
- 1 pound-foot ≡ 1 pound-force-foot ≈ 1.35581795 N⋅m
- 1 ounce-inch ≡ 1 ounce-force-inch ≈ 7.06155181 mN⋅m (millinewton-metres)
- 1 dyne-centimetre = 10−7 N⋅m
See also
[edit]- Bending moment
- Spring scale
- Torque tester
- Newton-second, the derived SI unit of impulse
Notes
[edit]- ^ The nonstandard notation "Nm" occurs in some fields.
References
[edit]- ^ a b BIPM – unit symbols
- ^ For example: Eshbach's handbook of engineering fundamentals - 10.4 Engineering Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer "In SI units the basic unit of energy is newton-metre".
- ^ Fundamentals of Physics, 9th edition by Halliday Resnick Ralker, p. 309. "The SI unit of torque is the newton-meter. In our discussion of energy we called this combination the joule. But torque is not work and torque should be expressed in newton-meters, not joules. google books link
- ^ a b BIPM - special names
- ^ Mechanical Engineering Formulas Pocket Guide, p6
- ^ Concise encyclopedia of plastics, by Donald V. Rosato, Marlene G. Rosato, Dominick V. Rosato, p621
| Base units | |
|---|---|
| Derived units with special names | |
| Other accepted units | |
| See also | |
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

