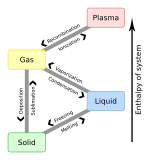
Enthalpy of sublimation
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of sublimation, or heat of sublimation, is the heat required to sublimate (change from solid to gas) one mole of a substance at a given combination of temperature and pressure, usually standard temperature and pressure (STP). It is equal to the cohesive energy of the solid. For elemental metals, it is also equal to the standard enthalpy of formation of the gaseous metal atoms.[1] The heat of sublimation is usually expressed in kJ/mol, although the less customary kJ/kg is also encountered.
Sublimation enthalpies
| symbol | substances | Sublimation enthalpy (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Li | lithium | 159[1] |
| Na | sodium | 107[1] |
| K | potassium | 89[1] |
| Rb | rubidium | 81[1] |
| Cs | caesium | 76[1] |
| Mg | magnesium | 148[1] |
| Ca | calcium | 178[1] |
| Sr | strontium | 164[1] |
| Ba | barium | 180[1] |
| Fe | iron | 416[1] |
| Ni | nickel | 430[1] |
| Cu | copper | 338[1] |
| Zn | zinc | 131[1] |
| Ag | silver | 285[1] |
| W | tungsten | 849[1] |
| Au | gold | 366[1] |
| C | graphite | 717[1] |
| C | diamond | 715[1] |
| Si | silicon | 456[1] |
| Sn | tin | 302[1] |
| Pb | lead | 195[1] |
| I2 | iodine | 62.4[2] |
| C10H8 | naphthalene | 72.9[2] |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide | 25[2] |
| H2O | water | 51.1 |
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.