Encoder (digital)
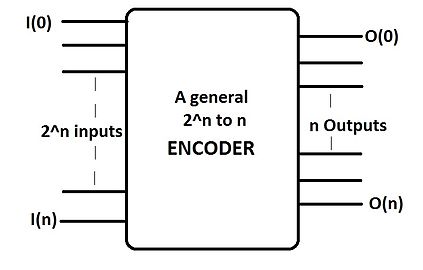
An encoder (or "simple encoder") in digital electronics is a one-hot to binary converter. That is, if there are 2n input lines, and at most only one of them will ever be high, the binary code of this 'hot' line is produced on the n-bit output lines. A binary encoder is the dual of a binary decoder.
If the input circuit can guarantee at most a single-active input, a simple encoder is a better choice than a priority encoder, since it requires less logic to implement. However, a simple encoder can generate an incorrect output when more than a single input is active, so a priority encoder is required in such cases.
Types of encoder
[edit]2n-to-n encoders
[edit]A -to-n encoder has n number of outputs in correspondence to the number of inputs. It thus reduces the number of transmission lines and can be compared to a multiplexer. Only one of the inputs become "high" (logic state "1") at a time.
For example, a 4-to-2 simple encoder takes 4 input bits and produces 2 output bits. The illustrated gate level example implements the simple encoder defined by the truth table, but it must be understood that for all the non-explicitly defined input combinations (i.e., inputs containing 0, 2, 3, or 4 high bits) the outputs are treated as don't cares.[1]
4-to-2 encoder
[edit]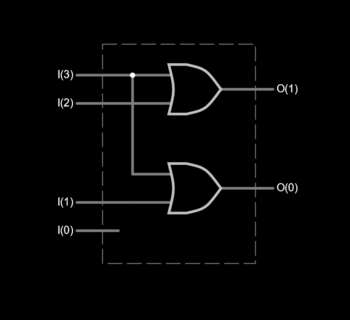
| Input | Output | |||||
| I3 | I2 | I1 | I0 | O1 | O0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | x | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
8-to-3 encoder
[edit]
| Input | Output | |||||||||
| I7 | I6 | I5 | I4 | I3 | I2 | I1 | I0 | O2 | O1 | O0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | x | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Binary Encoders And Their Applications". Electronics Hub. 2015-06-29. Retrieved 2017-05-01.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

