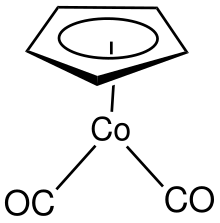
Cyclopentadienylcobalt dicarbonyl
| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.933 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CpCo(CO)2 | |
| Molar mass | 180.05 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark red to black liquid |
| Density | 1.35 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −22 °C (−8 °F; 251 K) |
| Boiling point | 139 to 140 °C (282 to 284 °F; 412 to 413 K) (710 mmHg) 37-38.5 °C (2 mmHg) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H301, H311, H331, H334, H341, H351, H412 | |
| Flash point | 26.7 °C (80.1 °F; 299.8 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cyclopentadienylcobalt dicarbonyl is an organocobalt compound with formula (C5H5)Co(CO)2, abbreviated CpCo(CO)2. It is an example of a half-sandwich complex. It is a dark red air sensitive liquid. This compound features one cyclopentadienyl ring that is bound in an η5-manner and two carbonyl ligands. The compound is soluble in common organic solvents.[1]
Preparation
[edit]CpCo(CO)2 was first reported in 1954 by Piper, Cotton, and Wilkinson who produced it by the reaction of cobalt carbonyl with cyclopentadiene.[2] It is prepared commercially by the same method:
- Co2(CO)8 + 2 C5H6 → 2 C5H5Co(CO)2 + H2 + 4 CO
Alternatively, it is generated by the high pressure carbonylation of bis(cyclopentadienyl)cobalt (cobaltocene) at elevated temperature and pressures:[1]
- Co(C5H5)2 + 2 CO → C5H5Co(CO)2 + "C5H5"
The compound is identified by strong bands in its IR spectrum at 2030 and 1960 cm−1.[3]
Reactions
[edit]CpCo(CO)2 catalyzes the cyclotrimerization of alkynes.[4][5] The catalytic cycle begins with dissociation of one CO ligand forming bis(alkyne) intermediate.[6]
- CpCo(CO)2 + 2 R2C2 → CpCo(R2C2)2 + 2 CO
This reaction proceeds by formation of metal-alkyne complexes by dissociation of CO. Although monoalkyne complexes CpCo(CO)(R1C2R2) have not been isolated, their analogues, CpCo(PPh3)(R1C2R2) are made by the following reactions:[6]
- CpCo(CO)2 + PR3 → CO + CpCo(CO)(PR3)
- CpCoL(PR3) + R2C2 → L + CpCo(PR3)(R2C2) (where L = CO or PR3)
CpCo(CO)2 catalyzes the formation of pyridines from a mixture of alkynes and nitriles. Reduction of CpCo(CO)2 with sodium yields the dinuclear radical [Cp2Co2(CO)2]−, which reacts with alkyl halides to give the dialkyl complexes [Cp2Co2(CO)2R2]. Ketones are produced by carbonylation of these dialkyl complexes, regenerating CpCo(CO)2.[6]
Related compounds
[edit]The pentamethylcyclopentadienyl analogue Cp*Co(CO)2 (CAS RN#12129-77-0) is well studied. The Rh and Ir analogues, CpRh(CO)2 (CAS RN#12192-97-1) and CpIr(CO)2 (CAS RN#12192-96-0), are also well known.
References
[edit]- ^ a b King, R.B.; Stone, F.G.A (1963). "Cyclopentadienyl Metal Carbonyls and Some Derivatives". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 7. pp. 99–115. doi:10.1002/9780470132388.ch31. ISBN 9780470132388.
((cite book)):|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Piper, T.S.; Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. (1955). "Cyclopentadienyl-carbon monoxide and related compounds of some transitional metals". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 1 (3): 165. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(55)80053-X.
- ^ "Cobalt, dicarbonyl(η5-2,4-cyclopentadien-1-yl)-".
- ^ Vollhardt, K. Peter C. (1984). "Cobalt-assisted [2+2+2] cycloadditions: a synthesis strategy grows to maturity". Angewandte Chemie. 96: 525–41. doi:10.1002/ange.19840960804.
- ^ Staeb, T.H.; Chavez, J.; Gleiter, R.; Nuber, Bernhard (2005). "The Role of [η2-Bis(tert-butylsulfonyl)acetylene](carbonyl)(η5-cyclopentadienyl) cobalt(I) as an Intermediate in the Alkyne Dimerisation". Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2005 (20): 4090. doi:10.1002/ejic.200500394.
- ^ a b c Pauson, P.L. “Dicarbonyl(cyclopentadienyl)cobalt(I).” Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. 2001. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rd078
| Cobalt(I) | |
|---|---|
| Cobalt(II) | |
| Cobalt(0, III) | |
| Cobalt(II, III) | |
| Cobalt(III) | |
| Cobalt(III,IV) | |
| Cobalt(IV) | |
| Cobalt(V) | |
Salts and covalent derivatives of the cyclopentadienide ion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
