Code segment
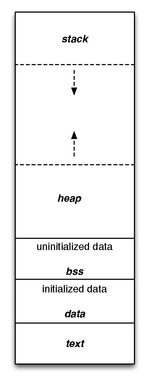
In computing, a code segment, also known as a text segment or simply as text, is a portion of an object file or the corresponding section of the program's virtual address space that contains executable instructions.[1]
Segment
[edit]The term "segment" comes from the memory segment, which is a historical approach to memory management that has been succeeded by paging. When a program is stored in an object file, the code segment is a part of this file; when the loader places a program into memory so that it may be executed, various memory regions are allocated (in particular, as pages), corresponding to both the segments in the object files and to segments only needed at run time. For example, the code segment of an object file is loaded into a corresponding code segment in memory.
The code segment in memory is typically read-only and has a fixed size, so on embedded systems it can usually be placed in read-only memory (ROM), without the need for loading. If the code segment is not read-only, then the particular architecture allows self-modifying code. Fixed-position or position-independent code may be shared in memory by several processes in segmented or paged memory systems.[1][2] As a memory region, the code segment may be placed below the heap or stack in order to prevent heap and stack overflows from overwriting it.[3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Jason W. Bacon (2012-03-13). "Chapter 10. Subprogram Calls and the Stack". cs.uwm.edu. Section 10.4. Memory Segments. Archived from the original on 2014-05-02. Retrieved 2014-05-02.
- ^ Kai Wang (2012-09-20). "Code Segment and Data Segment: Memory Layout of a Program". beingdeveloper.com. Archived from the original on 2014-05-02. Retrieved 2014-05-02.
- ^ Yu-An Tan; Ji-yan Zheng; Yuan-Da Cao; Xue-lan Zhang (October 2005). Buffer overflow protection based on adjusting code segment limit. IEEE International Symposium on Communications and Information Technology. IEEE. doi:10.1109/ISCIT.2005.1567023.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
