Antenna blind cone
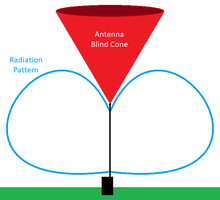
In telecommunications, antenna blind cone (sometimes called a cone of silence or antenna blind spot) is the volume of space, usually approximately conical with its vertex at the antenna, that cannot be scanned by an antenna because of limitations of the antenna radiation pattern and mount.[1]
An Air Route Surveillance Radar (ARSR) is an example of an antenna blind cone. The horizontal radiation pattern of an ARSR antenna is very narrow, and the vertical radiation pattern is fan-shaped, reaching approximately 70° of elevation above the horizontal plane. As the fan antenna is rotated about a vertical axis, it can illuminate targets only if they are 70° or less from the horizontal plane. Above that elevation, they are in the antenna blind cone.
The antenna blind cone is also referred to as the "cone of silence", especially in America. This term is also used for weather radars. NEXRAD radars make two-dimensional scans at varying angles ranging from 0.5° above level to 19.5° above level (during a significant weather event). These levels become much closer to the ground, and closer to each other, as they get closer to the radar site, rendering them of little use for the three-dimensional profiling such multi-level scanning is meant to provide. Thus, a weather event located very close to and/or directly overhead of the radar site will be mostly situated in the "cone of silence." This is part of the reason why most U.S. weather radars partially overlap each other's territories.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Rudge, Alan W., ed. (1983). The Handbook of Antenna Design. Vol. 2. p. 216. ISBN 9780906048870.
- ^ "National Doppler Radar Sites". noaa.gov.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
