Φερές
| Φερές | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 39°22′43″N 22°44′57″E | |
| Χώρα | Ελλάδα |
| Διοικητική υπαγωγή | Δήμος Ρήγα Φεραίου |

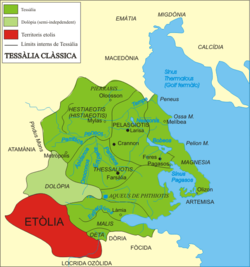
Στην Αρχαία Ελλάδα οι Φερές ή Φεραί ήταν Πόλη-Κράτος στην νοτιοανατολική αρχαία Θεσσαλία.[1][2] Σύμφωνα με την παράδοση πήραν το όνομα τους από τον Φέρητα, τον γιο του Κρηθέα ή από τη Φερά, την κόρη του Αιόλου. Ήταν πάρα πολύ σπουδαία πόλη, που ανήκε στην Πελασγιώτιδα τετραρχία και είχε ως επίνειο τις Παγασές.[3] Αναφέρεται μάλιστα και από τον Όμηρο στον κατάλογο των πόλεων που πήραν μέρος στον Τρωικό Πόλεμο [4]. Σύμφωνα με τον Στράβων βρισκόταν κοντά στην Βοιβηΐς λίμνη σε απόσταση 90 Σταδίων από τις Παγασές, το λιμάνι της στον Παγασητικό κόλπο.
Γύρω στο 450 π.Χ. αναφέρεται η πόλη σε επιγραφή των Δελφών. Στις αρχές του Πελοποννησιακού Πολέμου, η θεσσαλική αυτή πόλη ήταν σύμμαχος των Αθηναίων. Μετά όμως από το τέλος του πολέμου εγκαθιδρύθηκε εκεί τυραννίδα με πρώτο τύραννο το Λυκόφρονα. Το 352 π.Χ. η πόλη καταλήφθηκε από τον Φίλιππο Β΄ και ελευθερώθηκε από τον Δημήτριο τον Πολιορκητή το 302 π.Χ. Από το τέλος του 2ου π.Χ. αι. δεν γίνεται λόγος για τις Φερές. Το 191 π.Χ. η πόλη καταλήφθηκε από τον Ρωμαίο ύπατο Άκιο Γλαβρίωνα. Στις Φερές λατρευόταν η Φεραία Άρτεμις. Έχουν ανακαλυφθεί πάρα πολλά νομίσματα των Φερών (η πόλη άρχισε να κόβει νομίσματα από το 480 π.Χ. μέχρι το 200 π.Χ.) από τα οποία τα παλιότερα ανάγονται στην εποχή των Περσικών Πολέμων. Η σύγχρονη κωμόπολη Βελεστίνο βρίσκεται στο χώρο των αρχαίων Φερών.[5][6] Χτίστηκε κατά τον Μεσαίωνα. Εκεί γεννήθηκε ο Ρήγας Βελεστινλής.
Παραπομπές
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- ↑ Mogens Herman Hansen & Thomas Heine Nielsen (2004). "Thessaly and Adjacent Regions". An inventory of archaic and classical poleis. New York: Oxford University Press. σ. 704
- ↑ https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0073%3Aentry%3D*ferai%2F
- ↑ https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0064:entry=pherae-geo
- ↑ Ομήρου Ιλιάδα, Ραψωδία Β, στ. 711 και εξής
- ↑ https://imperium.ahlfeldt.se/places/22809.html
- ↑ Richard Talbert, ed. (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World. Princeton University Press. σ. 55
Πηγές
[Επεξεργασία | επεξεργασία κώδικα]- Mogens Herman Hansen & Thomas Heine Nielsen (2004). "Thessaly and Adjacent Regions". An inventory of archaic and classical poleis. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Richard Talbert, ed. (2000). Barrington Atlas of the Greek and Roman World. Princeton University Press.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

