Humulon
aus Wikipedia, der freien Enzyklopädie
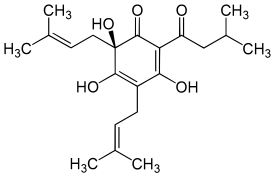
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | Humulon | |||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C21H30O5 | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 362,47 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | ||||||||||||||||
Humulon (auch α-Lupulinsäure) ist ein bakteriostatischer Bitterstoff.
Vorkommen
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
Das Harz des reifen Hopfens Humulus lupulus enthält Humulon. Dessen durch Erhitzung entstehende Umlagerungsprodukte (insbesondere cis- und trans-Isohumulon) geben dem Bier seinen charakteristischen bitteren Geschmack.[3] Er wird zu den Hopfenbitterstoffen gezählt.

Strukturell ist Humulon ein Hydroxy-phloroglucin mit drei isoprenoiden Seitenketten. Eine entzündungshemmende Wirkung des Humulon wurde als Unterdrückung der Transkription des der Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) zugehörigen Gens nachgewiesen,[4] womit die Bildung von Prostaglandinen inhibiert wird.
Weblinks
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ Eintrag zu Humulone. In: Römpp Online. Georg Thieme Verlag, abgerufen am 29. Dezember 2014.
- ↑ Dieser Stoff wurde in Bezug auf seine Gefährlichkeit entweder noch nicht eingestuft oder eine verlässliche und zitierfähige Quelle hierzu wurde noch nicht gefunden.
- ↑ Briggs, D.E., C.A. Boulton, P.A. Brookes, and R. Stevens, Brewing Science and Practice. 2004, Cambridge, UK: Woodhead Publishing Limited, ISBN 978-0-8493-2547-2.
- ↑ K. Yamamoto, J. Wang, S. Yamamoto, H. Tobe: Suppression of Cyclooxygenase-2 Gene Transcription by Humulone. In: Kenneth V. Honn, Lawrence J. Marnett, Santosh Nigam, Edward Dennis, Charles Serhan (Hrsg.): Eicosanoids and other bioactive lipids in cancer, inflammation, and radiation injury, Band 5. Springer, 2002, ISBN 978-0-306-47283-1, S. 73–76.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.
