Brückenkopfatome
aus Wikipedia, der freien Enzyklopädie
Brückenkopfatome (englisch bridgehead atoms) sind in der Chemie – genauer in den Strukturformeln chemischer Verbindungen – vorhandene Atome in größeren Molekülen, z. B. in verbrückten bicyclischen Ringsystemen. Meist sind die Brückenkopfatome Kohlenstoffatome, es gibt aber auch Verbindungen mit zwei Stickstoff-Brückenkopfatomen, beispielsweise Diazabicyclooctan (DABCO).[1] Auch die Trögersche Base enthält zwei Stickstoff-Brückenkopfatome, die zudem Stereozentren darstellen, die nicht invertieren können, da die pyramidale Konfiguration stabil ist.[2]
-
Norbornan – die beiden blauen Pfeile weisen auf die Brückenkopfatome (Kohlenstoffatome)
-
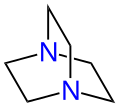
Diazabicyclooctan (DABCO) mit den beiden blau markierten Brückenkopfatomen (Stickstoffatome)
-
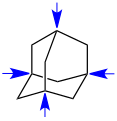
Adamantan – die vier blauen Pfeile weisen auf die Brückenkopfatome (Kohlenstoffatome)
-
Enantiomere der Trögerschen Base mit je zwei blau markierten Brückenkopfatomen (Stickstoffatome)
-
Twistan – die vier blauen Pfeile weisen auf die Brückenkopfatome (Kohlenstoffatome)
-
Tetrahedran, C4H4, enthält vier Brückenkopfatome (Kohlenstoffatome)
Adamantan enthält vier Kohlenstoff-Brückenkopfatome, ebenso wie Twistan. Campher und Kokain sind Naturstoffe, die je zwei Kohlenstoff-Brückenkopfatome enthalten.
Oft ist die Ausbildung einer Doppelbindung in einem Molekül unter Beteiligung eines Brückenkopfatoms schwierig, d. h. derartige Cycloalkene sind häufig instabil. Diese Thematik ist Gegenstand der Bredtschen Regel.[3]
Brückenkopf-Kohlenstoffatome finden sich in[4]
- kondensierten oder anellierten polycyclischen Alkanen (einfaches Beispiel: Decalin, in dem sich zwei Cyclohexanringe zwei Kohlenstoffatome miteinander teilen)
oder in
- überbrückten bicyclischen Ringsystemen (einfaches Beispiel: Norbornan).
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ Jonathan Clayden, Nick Greeves, Stuart Warren: Organische Chemie, Springer Spektrum, 2013, 2. Auflage, S. 920–921. ISBN 978-3-642-34715-3.
- ↑ Michael B. Smith: March's advanced organic chemistry, John Wiley & Sons, 7. Auflage, 2013, S. 129, ISBN 978-0-470-46259-1.
- ↑ Siegfried Hauptmann: Organische Chemie, 2. durchgesehene Auflage, VEB Deutscher Verlag für Grundstoffindustrie, Leipzig, 1985, S. 227, ISBN 3-342-00280-8.
- ↑ K. Peter C. Vollhardt: Organische Chemie, VCH, 1990, S. 164–165, ISBN 3-527-26912-6.
Text is available under the CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.